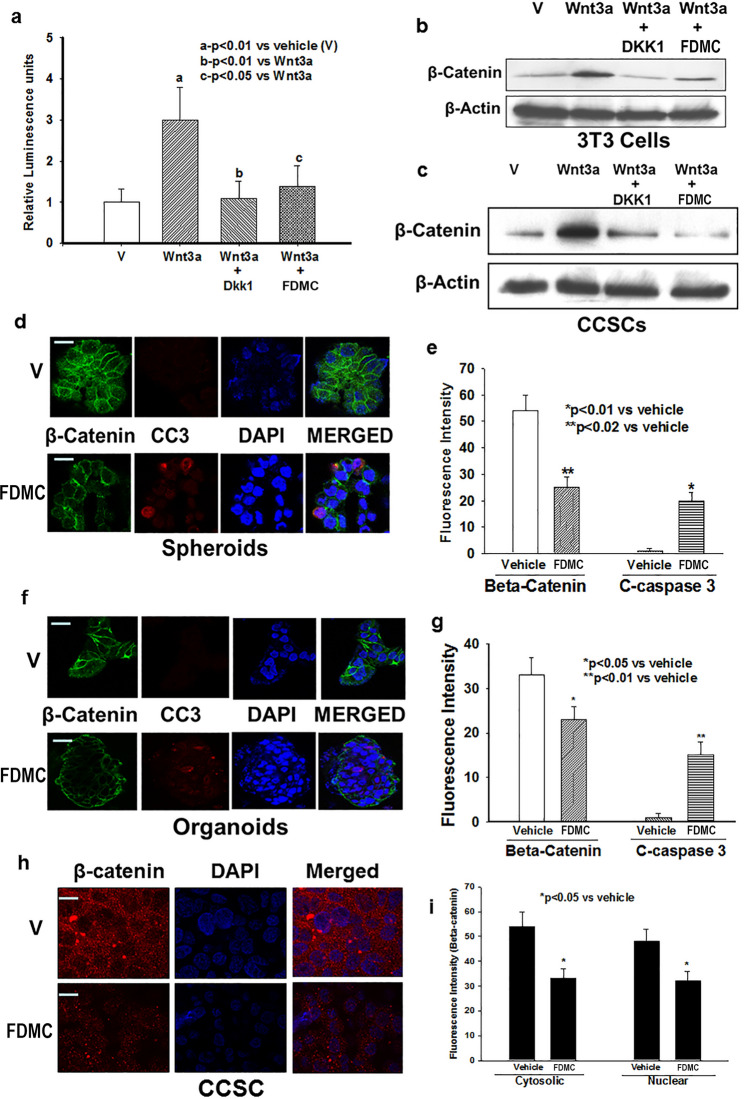
Figure 5.
Effects of FDMC on Wnt/β-catenin activity in CCSCs, spheroids and organoids, and induction of apoptosis, as evidenced by comparisons with vehicle-treated controls (V = vehicle). (a) Wnt receptor activity (luciferase units) significantly induced by agonist (Wnt3a) (ap < 0.01) and decreased by antagonist (DKK1) (bp < 0.01) in 3T3 cells. FDMC (50 µM) treatment for 24 h significantly suppressed agonist-induced receptor activity (cp < 0.01) in 3T3 cells. (b) Western blot data show that Wnt receptor agonist Wnt3a treatment induced β-catenin expression, whereas Wnt receptor antagonist DKK1 treatment abolished the Wnt3a-induced induction of β-catenin in 3T3 cells. FDMC inhibited Wnt3a-induced β-catenin expression in 3T3 cells. (c) Western blot data show that Wnt receptor agonist Wnt3a treatment induced β-catenin expression, whereas Wnt receptor antagonist DKK1 treatment abolished the Wnt3a-induced induction of β-catenin in CCSCs. FDMC inhibited Wnt3a-induced β-catenin expression in CCSCs. (d,e) Confocal microscopy data show that FDMC (50 µM) treatment to CCSC-derived spheroids significantly depleted β-catenin expression (green immunofluorescence staining) and induced apoptosis (cleaved caspase 3; red immunofluorescence staining; *p < 0.01 and **p < 0.02). (f,g) Confocal microscopy data show that FDMC (50 µM) treatment to CCSC-derived organoids significantly depleted β-catenin expression (green immunofluorescence staining) and induced apoptosis (cleaved caspase 3; red immunofluorescence staining; *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01). Results are mean ± SEM (bars; n = 3).