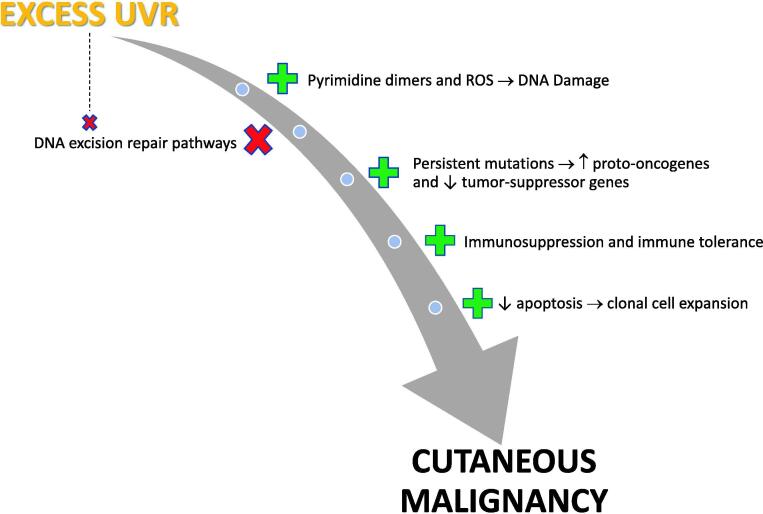
Fig. 2.
Schematic illustration of the multi-step process of photocarcinogenesis whereby exposure of the skin to ultraviolet radiation results in DNA damage via the formation of pyrimidine dimers and reactive oxygen species. Excisional repair of DNA may reverse some damage, but the reparative mechanisms are overwhelmed when ultraviolet radiation exposure is excessive. This allows the progression of mutagenesis, immune suppression, and clonal cell expansion, thus promoting tumor formation.