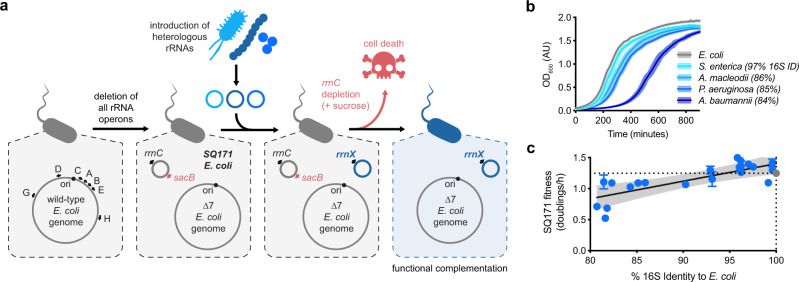
Fig. 1. Assessment of heterologous rRNA activity via SQ171 complementation.
a Schematic representation of the SQ171 complementation assay. SQ171 E. coli cells lack all 7 genomic ribosomal RNA (rRNA) operons and maintain a single rrnC operon on a SacB counter-selectable plasmid. Introduction of a heterologous rRNA (rrnX) and depletion of the E. coli rrnC plasmid using sucrose yields cells that rely upon the heterologous ribosome for survival. b Growth time course of SQ171 cells bearing increasingly divergent heterologous rRNAs (n = 2-8). c Correlation between heterologous 16S rRNA sequence identity to E. coli (%) and SQ171 fitness (doublings/h) upon complementation (99% CI, R2 = 0.62). E. coli rRNA control plotted in gray. Data represent the means of 1–8 biological replicates; error bars represent standard deviations for conditions with 3 or more replicates. Complete SQ171 complementation data (including precise number of replicates) are reported in Supplementary Table 1. OD optical density, AU arbitrary units, h hour. Source data are available in the Source Data File.