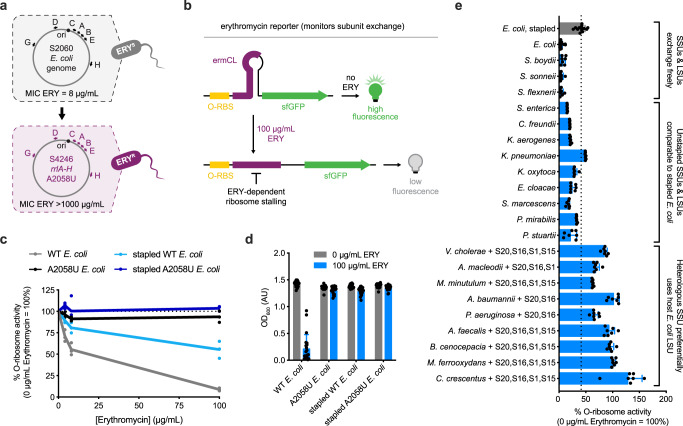
Fig. 6. The erythromycin-dependent orthogonal translation reporter system.
a Creation of the erythromycin (ERY)-resistant E. coli strain S4246. All 7 rrl (A-H) 23S ribosomal RNA (rRNA) genes were mutated (A2058U) via oligonucleotide recombineering to endow high erythromycin resistance (ERY; MIC > 1000 µg mL−1). b Schematic representation of the ERY-dependent superfolder GFP (sfGFP) reporter. In the absence of ERY, sfGFP is efficiently translated via orthogonal translation. Addition of ERY (100 µg mL−1) promotes translation stalling at the ermC leader peptide (ermCL), abrogating sfGFP translation by ERY-sensitive large subunits (LSUs). c Free and stapled ERY-sensitive LSUs show a marked reduction in sfGFP production at high inhibitor concentrations, whereas the corresponding ERY-resistant (23S A2058U) LSUs show no appreciable change in activity (n = 2 for A2058U E. coli at 4 µg/mL ERY; otherwise n = 3). d ERY-sensitive LSUs re-establish strain sensitivity to ERY due to free subunit exchange between episomally and genomically derived ribosomes (n = 21). e Evaluation of intersubunit exchange using the ERY-dependent reporter system. Heterologous ribosomes with high 16S sequence identity to E. coli (≥99.2%) appear to freely exchange with host subunits, while heterologous ribosomes with intermediate sequence identity (97.0–92.9%) preferentially associate with cognate subunits at a rate comparable to the stapled E. coli ribosome. More divergent heterologous ribosomes (90.3–79.3%) preferentially utilize E. coli large subunits (n = 28 for E. coli and n = 14 for E. coli, stapled; otherwise n = 7). Data for each ribosome is normalized to its corresponding sfGFP signal at 0 µg mL−1 ERY. Data reflect the mean and standard deviation of the indicated biological replicates. Comprehensive data reported in Supplementary Table 3. MIC = minimum inhibitory concentration; OD optical density, O-RBS orthogonal RBS, O-ribosome orthogonal ribosome, SSU small subunit. Source data are available in the Source Data File.