Figure 2.
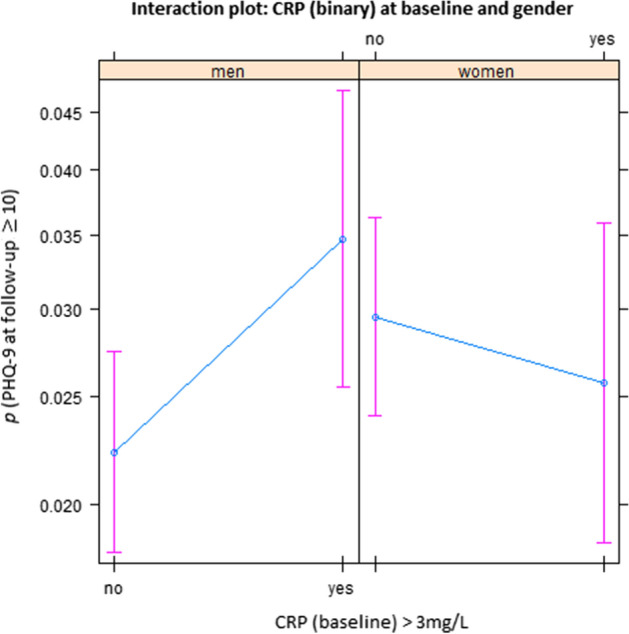
Association with baseline CRP levels and depression symptoms at follow-up in men and women. We observed gender differences regarding the association of elevated levels of CRP at baseline with new onset of depression at follow-up: in men, elevated CRP at baseline was associated with higher PHQ-9 scores at follow-up; whereas in women, no clear effect of baseline CRP on PHQ-9 at follow-up was apparent. The plot results show the probability (p) and 95% confidence intervals of depression (PHQ-9 ≥ 10) estimated based on the regression model of the total sample (reported in Table 2), depending on baseline CRP (normal versus elevated) and other predictors held fixed. (Figures were created using R version 3.6.1 https://www.R-project.org/).
