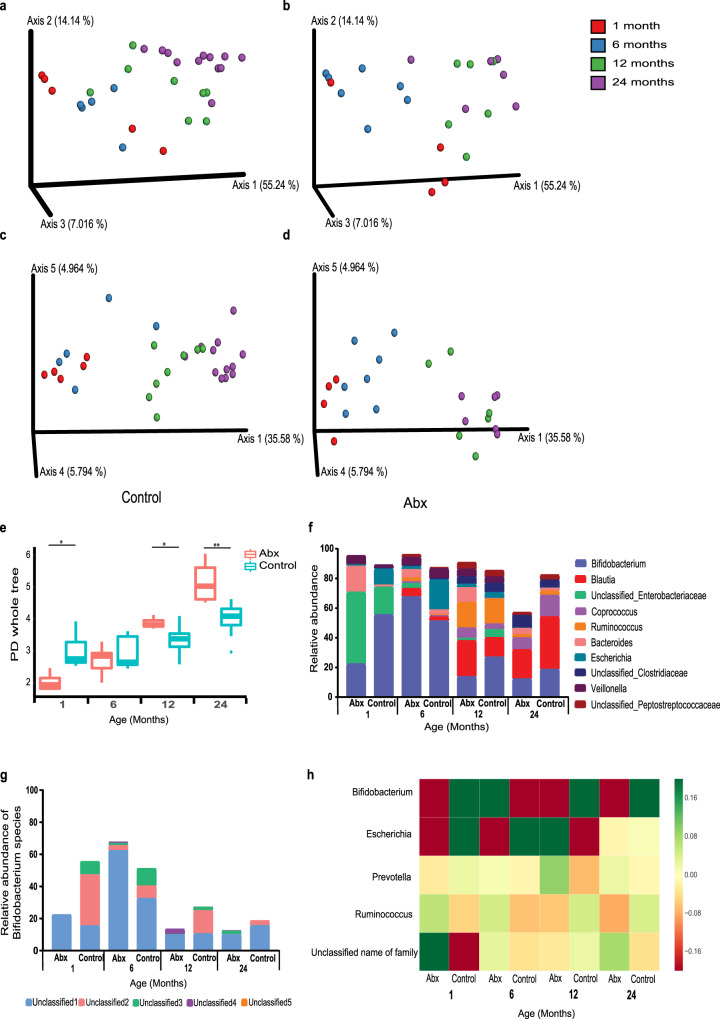
Fig. 3. Alterations in gut bacterial colonization in infants following antibiotic exposure.
16 S rRNA sequencing was performed to characterize bacterial changes. a, b Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA) based on Weighted UniFrac and (c, d) Unweighted UniFrac distance matrices in (a, c) control (n = 20), and (b, d) antibiotic-treated (n = 13) infants after 1 (red), 6 (blue), 12 (green), and 24 (purple) months from antibiotic exposure. (e) Alpha diversity comparison based on phylogenetic diversity. Significant differences in bacterial richness between control and antibiotic-treated groups are seen at 1 (p = 0.014), 12 (p = 0.014) and 24 (p = 0.001) months following antibiotic exposure. (f) Relative taxonomic composition based on 10 most abundant genera of control and antibiotic-treated groups. (g) Relative levels of Bifidobacterium species. (h) Average log10 change in the bacteria showing significant differences between groups (p < 0.05 and FDR correction). Green values imply over-representation, and red represents under representation. (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and ****p < 0.0001; minimum four samples in each group).