Fig. 1. The natural tendency for Coulomb interactions to cause a quasi-circular in-plane scattering pattern.
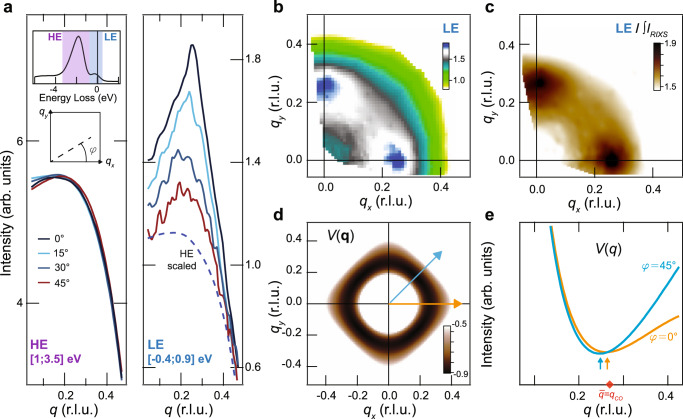
a RIXS scattering measured at 50 K as a function of momentum along different φ, obtained by integrating the energy loss spectra over the high-energy (E > 0.9 eV, HE) and low-energy (E < 0.9 eV, LE) regions. The inset displays the Cu-L3 RIXS energy-loss spectrum for q ≈ 0.05 rlu and φ = 0∘. The blue dashed line compares the featureless and φ-independent HE scattering signal to the LE curves. b CO structure in the qx–qy plane integrated over the LE region for 50 K. c Similar to (b) with LE data normalized to the total fluorescence, i.e., the RIXS spectrum integrated in the [−4,25] eV energy range (∫IRIXS, details in Supplementary Note 2). d The structure of the Coulomb interaction V(q) calculated using known parameters for Bi2212 (details in Supplementary Note 4). e Line cuts of (d) along φ = 0∘ and 45∘, as indicated by the blue and orange arrows. The red diamond in e indicates the experimentally determined = qCO.