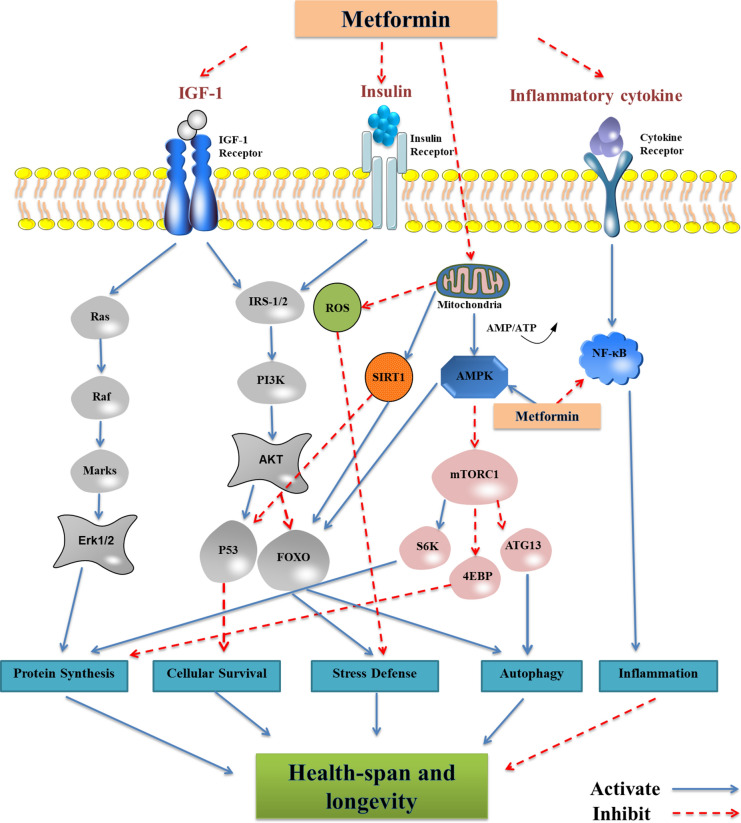
Fig. 1.
Metformin targets the major pathways of aging. Extracellularly, metformin decreases insulin levels and IGF-1 signaling while influencing multiple cytokines to participate in anti-aging processes. Intracellularly, metformin reduces ROS production by inhibiting mitochondrial complex I in the electron transport chain generation and AMPK activation, simultaneous increase in mTOR signal inhibition and SIRT1 activation, which resulting in a longer life-span; Metformin affects inflammatory responses, cellular stress responses and autophagy responses, etc. by acting both inside and outside the cell. These cellular processes are the primary biological responses associated with aging