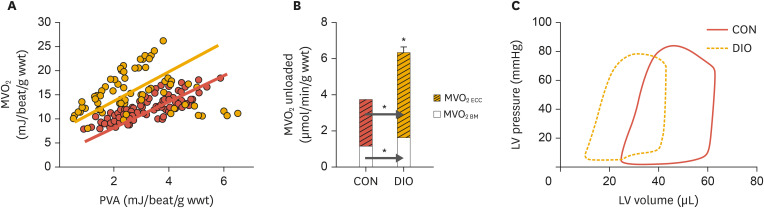
Fig. 3. Increased myocardial oxygen consumption and ventricular dysfunction in DIO mice. (A) Relationship between MVO2 and total cardiac work (measured as PVA) in isolated perfused hearts from lean CON (red line) and DIO mice (yellow line). (B) The increased oxygen consumption of the DIO hearts is explained by increased oxygen cost for excitation-contraction coupling as well as for basal metabolism. (C) Leftward shift of the pressure-volume loop of DIO heart relative to control, indicating concentric remodeling and ventricular stiffness. Modified from Hafstad et al.53.
MVO2, myocardial oxygen consumption; PVA, pressure-volume area; CON, control; DIO, diet-induced obese; LV, left ventricular.
*p<0.05 vs. CON.