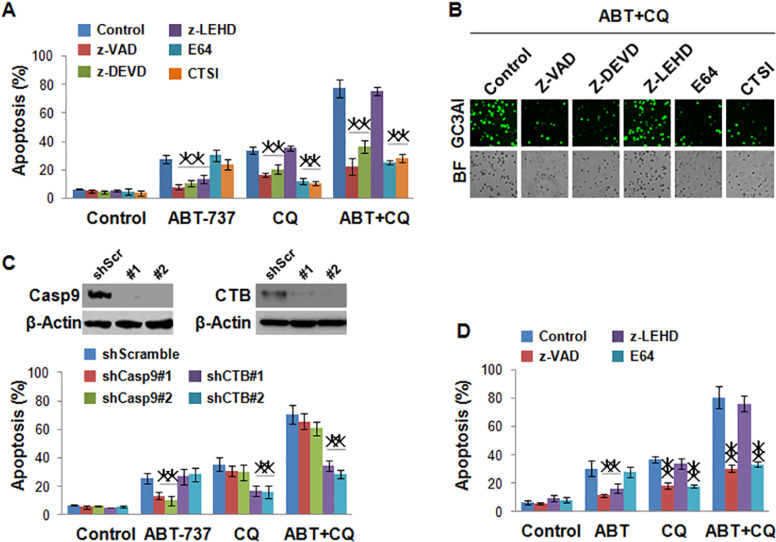
Figure 2.
ABT-737 and chloroquine synergistically induce lysosome-dependent cell death in renal cancers. (A) The effect of caspase inhibitors and lysosome protease inhibitors on apoptosis of A498 cells induced by 1 µmol/L of ABT-737 and 25 µmol/L of chloroquine alone or combination of these two reagents in 72 h. The cell death induced by chloroquine could be inhibited by all inhibitors, except for z-LEHD; the cell death induced by ABT-737 could be inhibited by all caspase inhibitor but not by lysosome inhibitor. (B) Apoptotic cells of A498 imaged by fluorescence microscope induced by a combination of 1 µmol/L of ABT-737 and 25 µmol/L of chloroquine with or without caspase inhibitors and lysosome protease inhibitors in 72 h. (C) The effect of knockdown of caspase 9 and cathepsin B (CTB) on the apoptosis of A498 induced by 1 µmol/L of ABT-737 and 25 µmol/L of chloroquine alone or combination of these two reagents in 72 h; shcaspase 9 decreased apoptosis induced by ABT-737; shCTB decreased apoptosis induced by chloroquine. (D) The effect of caspase inhibitors and lysosome protease inhibitors on apoptosis of 786-O cells induced by 1 µmol/L of ABT-737 and 25 µmol/L of chloroquine alone or a combination of these two reagents in 72 h. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01.