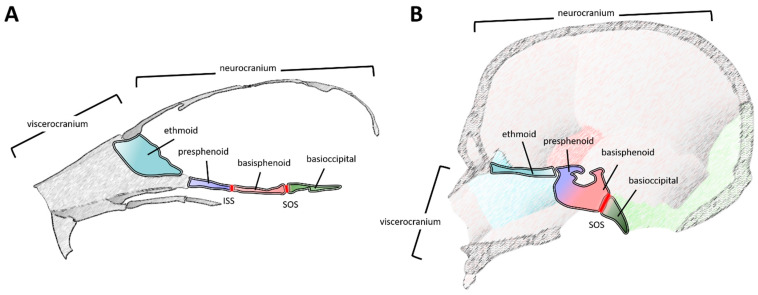
Figure 2.
Schematics illustrating a midsagittal plane of the cranial base, in relation to other cranial structures, in a mouse (A) and a human (B). Note, scales are not equivalent. The major elements within this plane are the ethmoid (teal), presphenoid (light blue), basisphenoid (light red), and basioccipital (green). Major growth zones (synchondroses) are highlighted (dark red), including the inter-sphenoid and spheno-occipital synchondrosis. Note, in panel B, the presphenoid and basisphenoid have fused into the sphenoid (gradient of light blue and red), so the inter-sphenoid synchondrosis is not demarcated. The relative units of the skull, including the neurocranium (calvaria and the cranial base) and the viscerocranium (facial bones) are denoted. Rostral is to the left and caudal is to the right. The lower jaw (mandible) is not depicted. Abbreviations: ISS, inter-sphenoid synchondrosis; SOS, spheno-occipital synchondrosis.