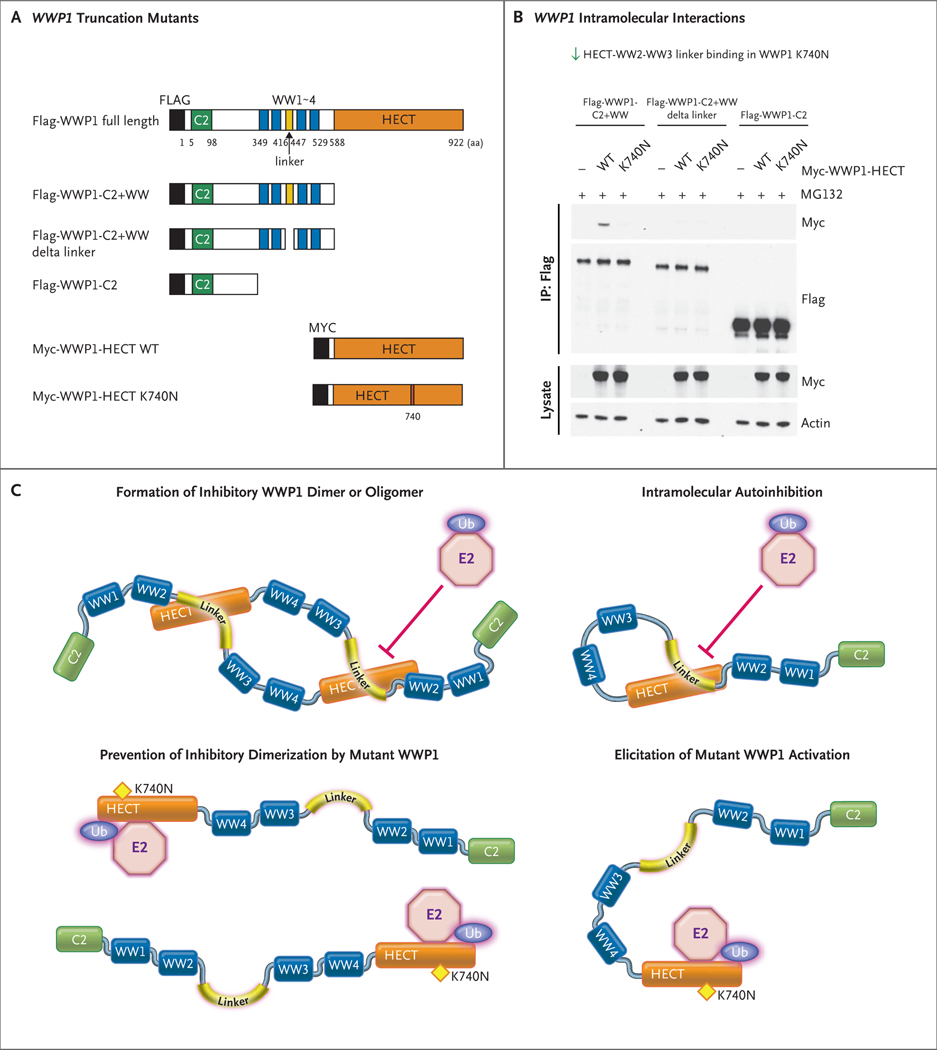
Figure 4. Promotion of WWP1 Catalytic Activity by WWP1 K740N through Disruption of Interaction between HECT and WW2–WW3 Linker Domains.
Panel A shows the truncation mutants of WWP1 with or without the K740N mutation within the HECT domain. Both Flag and Myc are short peptides used to tag proteins. Panel B shows an immunoprecipitation analysis of the interaction between multiple Flag-WWP1 truncation mutants and individual Myc-tagged HECT domains with or without the K740N mutation. Immunoprecipitation (IP) of Flag-WWP1 truncation mutants was performed with Flag antibody, followed by probing with Myc-tag antibody to detect the differential interaction between the HECT and WW2–WW3/C2 domains with or without the K740N mutation. Panel C shows a model of how the WWP1 E3 ligase activity is activated by the K740N variant by the disruption of WWP1 autoinhibition mediated by either homodimer or intramolecular processes. Ubiquitin conjugation enzyme, also known as E2, performs the second step in the ubiquitination process to coordinate with ubiquitin ligase for the transfer of ubiquitin moieties to the substrates. In turn, the inhibition of WWP1 activity is mediated by the interaction of its HECT domain with the WW2–WW3 linker domain.