Figure 4.
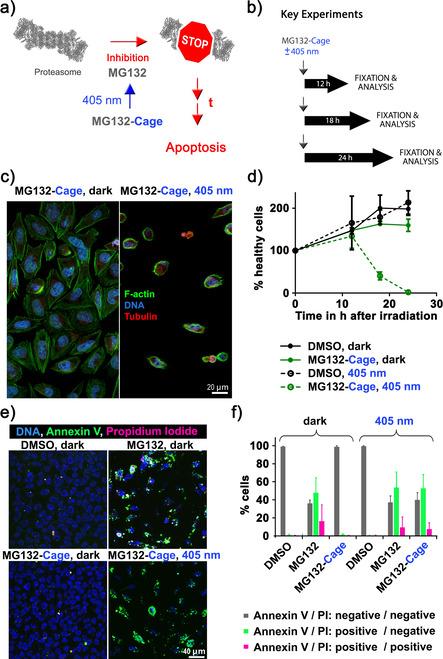
Induction of apoptosis in HeLa cells with blue light. a) Simplified mechanism of apoptosis induction by photoactivated MG132‐Cage. Blue‐light irradiation triggers MG132 release, which inhibits the proteasome leading to apoptosis of the respective cell after prolonged (t) exposure. b) Experimental setups to quantify blue‐light‐induced cell death over time. c) Confocal microscopy images of HeLa cells incubated with 10 μm MG132‐Cage and either maintained in the dark for 24 h (left) or exposed to 405 nm light for 10 min and then cultured for 24 h (right, the few remaining cells display hallmarks of apoptosis such as cell shrinkage and DNA condensation). d) Mean percentages of healthy cells at different time points under the indicated conditions. Photodeprotection of 10 μm MG132‐Cage results in complete cell death 24 hours after irradiation. Mean of two independent experiments is shown and error bars represent standard deviation. e) Maximum z‐projections of five images of HeLa cells stained with Hoechst dye to label all nuclei (DNA, blue), annexin V (green), and PI (red). HeLa cells were treated with 0.1 % DMSO or 10 μm MG132 and maintained in the dark, or treated with 10 μm MG132‐Cage and either exposed to 405 nm light for 10 min or kept in the dark. The 20 h time point was chosen to monitor annexin and PI labeling while cells are dying. f) Percentages of cells that were labeled by annexin V and/or PI for the indicated conditions. The mean of three independent experiments is shown and error bars represent standard deviation. For the different conditions a minimum of 123 and maximum of 409 cells were analyzed individually.
