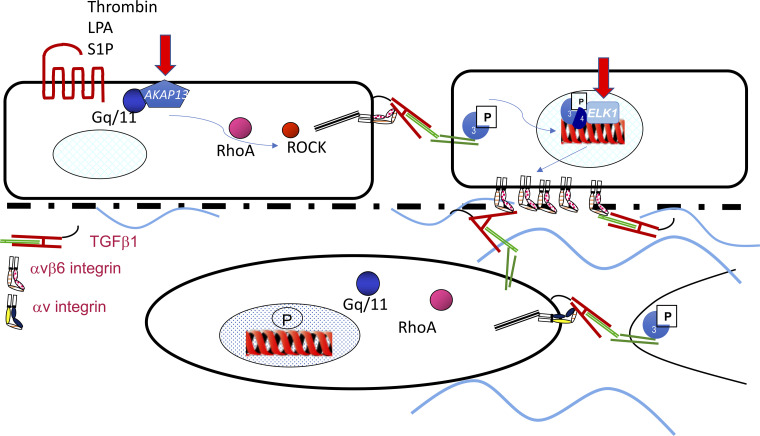
Fig. 1.
Injury to the alveolar surface leads to release of thrombin and lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), which act through G protein-coupled receptors PAR1 and LPAr2 to signal via Gq/11, RhoA, and Rho kinase (ROCK) to activate transforming growth factor (TGF)-β via the αvβ6 integrin. This in turn leads to TGF-β receptor activation in neighboring cells and Smad2/3 phosphorylation, which translocates to the nucleus, leading to increased transcription of the ITGB6 gene and increased expression of the αvβ6 integrin on the cell surface. This is able to activate fibroblast TGF-β if the epithelial basement membrane is denuded, leading to activation via fibroblast RhoA signaling and mesenchymal integrin-mediated TGF-β activation (αvβ1 and αvβ5) leading to autonomous fibroblast TGF-β activation. A-kinase anchoring protein 13 (AKAP13) is a Rho guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) that facilitates Gq/11 to RhoA signaling and may act as an amplification signal in epithelial cells, and ELK1 is a transcriptional repressor that is lost in pulmonary fibrosis. S1P, sphingosine-1 phosphate.