FIGURE 8.
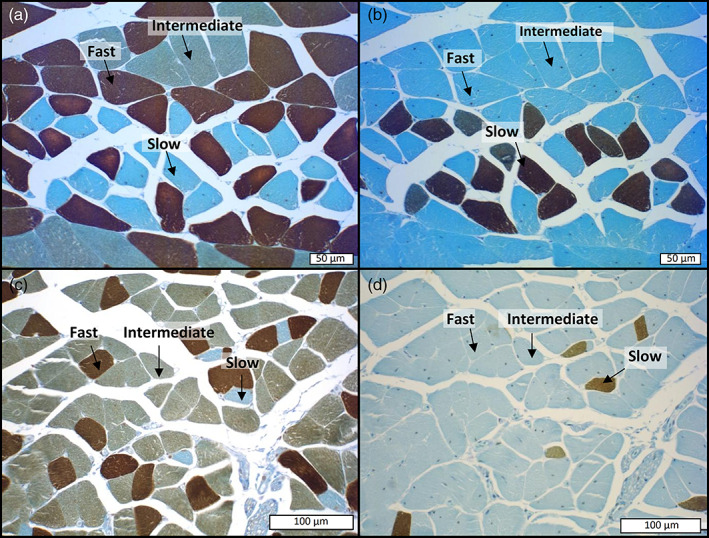
Illustration of the immunohistochemical method used for the typing of muscle fibers. The panel of four pictures corresponds to immunohistochemical labeling performed on serial sections of the muscles of Scincus scincus (a,b) and Eumeces schneideri (c,d), respectively. For each species, fast myosin was detected by a specific antibody (MY32 [Abcam]) in the first section (a,c) whereas slow muscle fibers were indicated in the following sections (b,d) by immunolabeling with specific anti‐slow myosin antibodies (NOQ 7.5.4D [Abcam]). On the left the pictures (a,c), correspond to the first section treated with antibodies raised against fast myosin, in which fast muscle fibers appear deeply stained in brown, intermediate fibers lightly stained in brown and slow muscle fibers negative (blue). In contrast, in the following sections (b,d), immunostained with antibodies raised against anti‐slow myosin only, slow muscle fibers are labeled in deep brown whereas intermediate and fast fibers are totally negative (blue color). The comparison between the consecutive sections (a vs. b and c vs. d) attests to the specificity of the immunolabeling and the clear‐cut identification of the three muscle fiber types
