Fig 1.
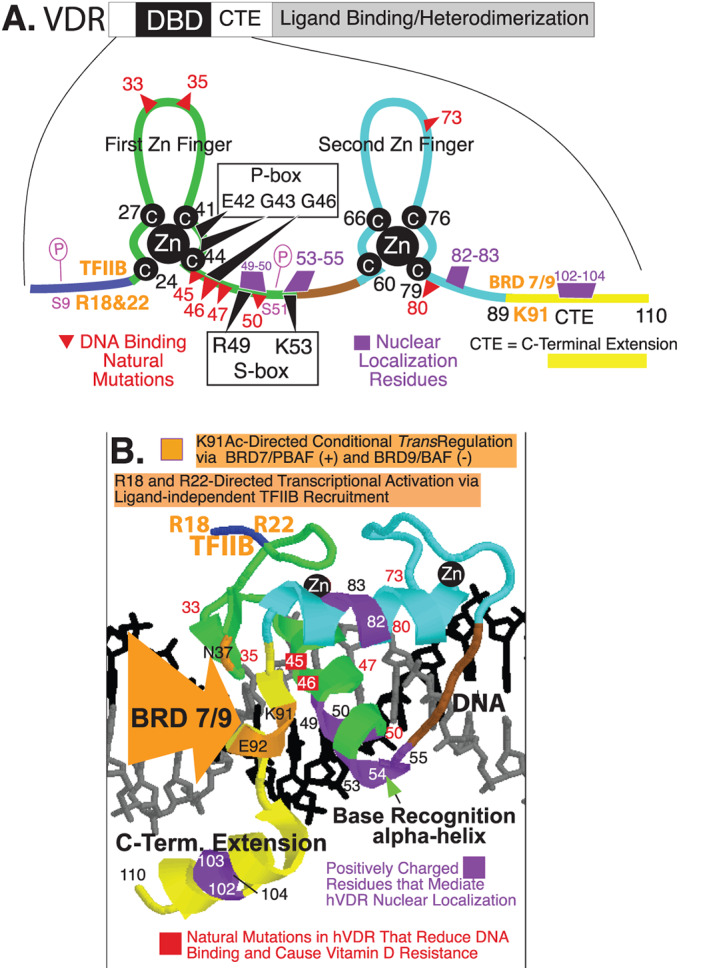
Human VDR DNA‐binding domain. (A) VDR schematic with the DBD/CTE magnified illustrating the two zinc fingers, DNA contact residues (P‐box and S‐box), DNA binding loss of function natural mutations, nuclear localization residues, transactivation residues (arginines 18 and 22; lysine 91), and phosphorylation sites (serines 9 and 51). (B) Model of VDR DBD/CTE bound to DNA. CTE = C‐terminal extension; DBD = DNA binding domain; VDR = vitamin D receptor; Zn = zinc.
