Fig. 6. Models of the filament uncapping.
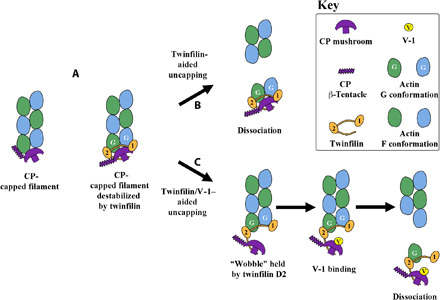
(A) Cartoon comparison of CP and CP/twinfilin association at the barbed end of a filament. (B) Twinfilin-aided uncapping is a result of twinfilin ADF-H domains inducing G-actin–like conformations in the terminal two actin protomers, weakening actin:actin interactions in the filament, leading to the dissociation of the complex. (C) Twinfilin/V-1–aided uncapping requires space for V-1 to reach its binding site on CP via a wobble state of the twinfilin-bound complex. Once V-1 is bound, CP is unable to reassociate with actin. In vitro effects of twinfilin alone on actin filaments and comparisons of uncapping models in the absence of twinfilin are shown in fig. S9.
