Fig. 1. Design of the flexible epidermal biomicrofluidic device for continuous blood glucose monitoring.
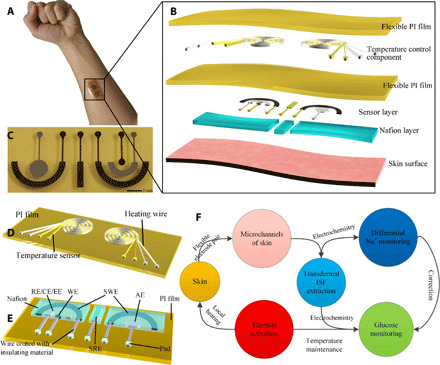
(A) Photo of the real application of the proposed device. (B) Detailed structure of the integrated epidermal biomicrofluidic device. (C) Photo of the fabricated flexible glucose detection patch. (D) Detailed structure of the temperature control component. (E) Detailed structure of the glucose detection patch consisting of an ISF extraction electrode pair (EE, extraction electrode; AE, auxiliary electrode), a glucose sensor (WE, working electrode; RE/CE, reference electrode/counter electrode), and a differential Na+ sensor (SWE, Na+ WE; SRE, Na+ RE). (F) Working mechanism of the integrated flexible epidermal biomicrofluidic device (photo credit: Zhihua Pu, Tianjin University).
