FIGURE 1.
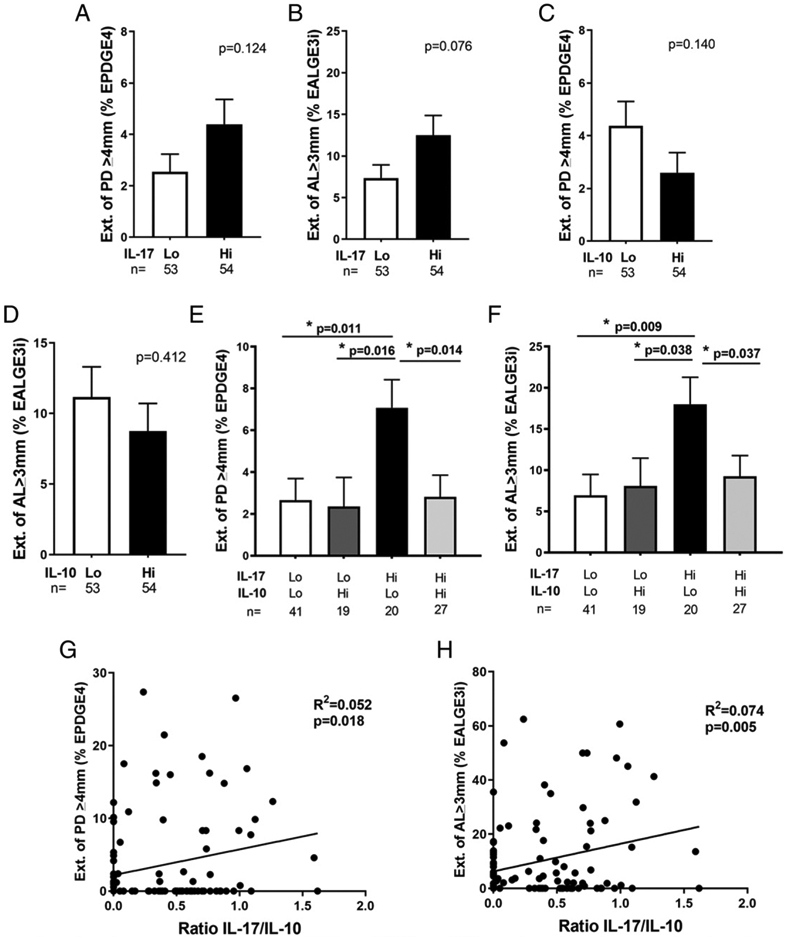
GCF levels of IL-17 interacted with IL-10 levels to determine the periodontal disease severity. The mediator levels of 107 clinical participants were dichotomized into low (Lo) or high (Hi) groups based on whether the log10-transformed GCF IL-17 or IL-10 levels exceeded the mean level of either cytokine of those participants. Extent of periodontal sites with probing depth ≥4 mm (A) or with attachment level ≥3 mm at interproximal sites was compared in Lo IL-17 to Hi IL-17 groups (B). The same comparisons of probing depth and attachment level were also compared in Lo IL-10 to Hi IL-10 groups (C and D). Clinical disease activity reflected by EPDGE4 (E) or attachment level at the interproximal sites ≥3 mm was compared among groups determined by the interactions between Lo or Hi IL-17 and IL-10 levels (F). GCF IL-17/IL-10 ratio was correlated to EPDGE4 (G) or of attachment level at the interproximal sites ≥3 mm (H). Data are shown as mean ± SE and were analyzed by either Student t test for two group comparisons or ANOVA for multigroup comparisons. Linear regression was applied for the correlation analysis. *p < 0.05.
