Figure 5.
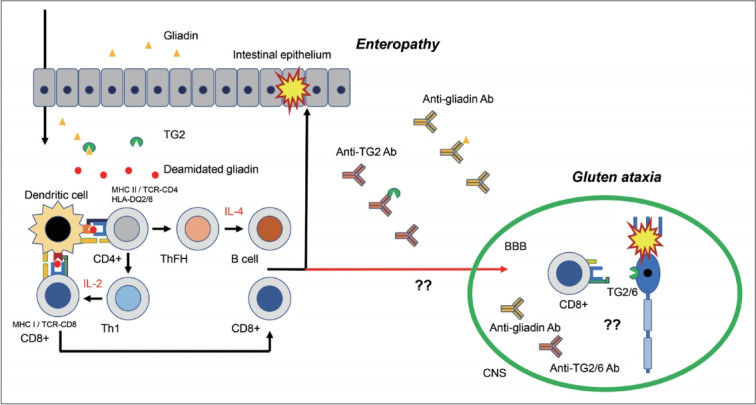
Possible autoimmune mechanisms underlying gluten ataxia. Gluten is a complex molecule contained in several grains. The major protein components are glutenin and gliadin. Digested gliadin is deamidated and cross-linked by TG2, leading to the creation of an immunostimulatory epitope for HLA-DQ2 or HLA-DQ8 on antigen-presenting cells. These epitopes are presented to CD4+ T cells, from which cytokines are released to facilitate the production of antibodies against gliadin and TG2. The pro-inflammatory cytokines activate cytotoxic CD8+ T cells, which in turn promote epithelium tissue damage. It is uncertain how CNS tolerance is broken down to develop cerebellar degenerations. TG: transglutaminase, CNS: central nervous system, BBB: blood-brain barrier, HLA: human leukocyte antigen.
