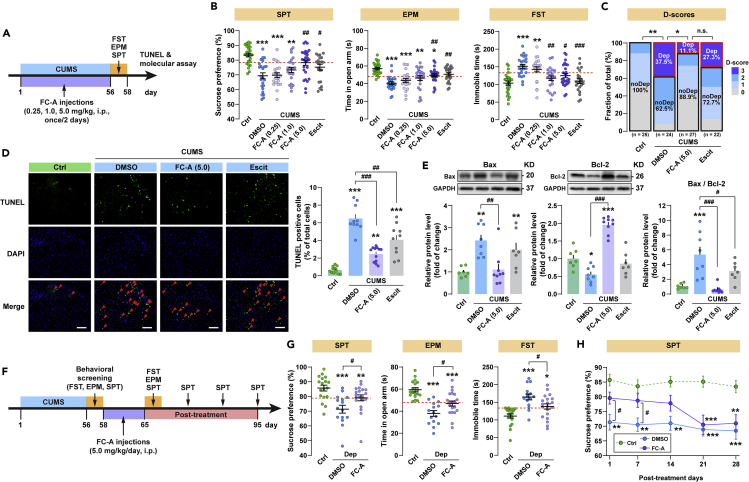
Figure 4.
Treatment with the fusicoccin-A (FC-A) relieves depressive-like behaviors and restores VLO neuronal apoptosis in CUMS mice
(A) Schematic of experiment for panel B–E. FC-A (0.25, 1.0 and 5.0 mg/kg body weight) was given i.p. every two days during the whole CUMS period. Escitalopram (Escit) was given once daily (20 mg/kg, i.p.) as the positive control. An equal volume of 1% DMSO was given i.p. as vehicle control. At the end of CUMS regime, the behavioral tests were carried out to assess the depressive phenotype and molecular changes in VLO.
(B) CUMS mice with 5.0 mg/kg FC-A treatment showed increased sucrose preference in SPT (post hoc, DMSO versus FC-A 5.0 mg/kg, t 136 = 3.716, p < 0.01), increased open arm time in EPM (post hoc, DMSO versus FC-A 5.0 mg/kg, t 136 = 4.982, p < 0.01), and decreased immobile time in FST (post hoc, DMSO versus FC-A 5.0 mg/kg, t 136 = 4.354, p < 0.05) compared with DMSO group. Data were analyzed with one-way ANOVA, followed by Sidak's post hoc test.
(C) 5.0 mg/kg FC-A treatment significantly changed the constituent ratio of depressive phenotypes (Fisher's exact test, DMSO versus FC-A 5.0 mg/kg, p < 0.05) and effectively reduced the number of Dep (D-3) mice as compared with DMSO group (n = 11/27 versus 2/24). No-depressive mice (noDep) were defined as those with D-score 0, 1, and 2.
(D) Left: confocal images showing the TUNEL-positive cells in the VLO of the mice in the 4 groups: non-stressed Ctrl, DMSO + CUMS, FC-A (5.0 mg/kg) + CUMS, and Escit + CUMS. n = 10–12 per group. Red arrow indicates the TUNEL-positive apoptotic cell. Scale bar: 200 μm. Right: quantification of TUNEL-positive cells demonstrated that treatment with FC-A rescued the CUMS-induced neural apoptosis in VLO (one-way ANOVA, Tukey's post hoc test, FC-A versus DMSO, t 40 = 11.11, p < 0.01).
(E) The CUMS-induced abnormal expression of Bax (left), Bcl-2 (middle), and ratio of Bax/Bcl-2 (right) were effectively rescued by systemic FC-A treatment. Protein levels were analyzed with one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post hoc test.
(F) Schematic of experiment for panel G and H. After CUMS and behavioral screening, Dep mice were treated with FC-A (5.0 mg/kg, i.p., once per day) for 7 days. After the FC-A treatment, depressive-like behaviors were assessed by SPT, EPM, and FST.
(G) Dep mice with FC-A treatment showed increased sucrose preference in SPT (post hoc, FC-A versus DMSO, t 50 = 3.499, p < 0.05), increased open arm time in EPM (post hoc, FC-A versus DMSO, t 50 = 3.774, p < 0.05), and decreased immobile time in FST (post hoc, FC-A versus DMSO, t 50 = 3.670, p < 0.05). Depressive behaviors were analyzed with one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's post hoc test.
(H) Sucrose preference in the FC-A + CUMS group was significantly higher than the DMSO + CUMS group 7 days after the FC-A treatment (two-way RM ANOVA, followed by Sidak's post hoc test, day 7: FC-A vs. DMSO, t 250 = 2.346, p < 0.05). Data represent mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, ∗∗∗p < 0.0001 compared with the Ctrl group; #p < 0.05, ##p < 0.05, ###p < 0.0001 compared with the DMSO group. n.s., not significant. LO and relieves depressive-like behaviors following CUMS.