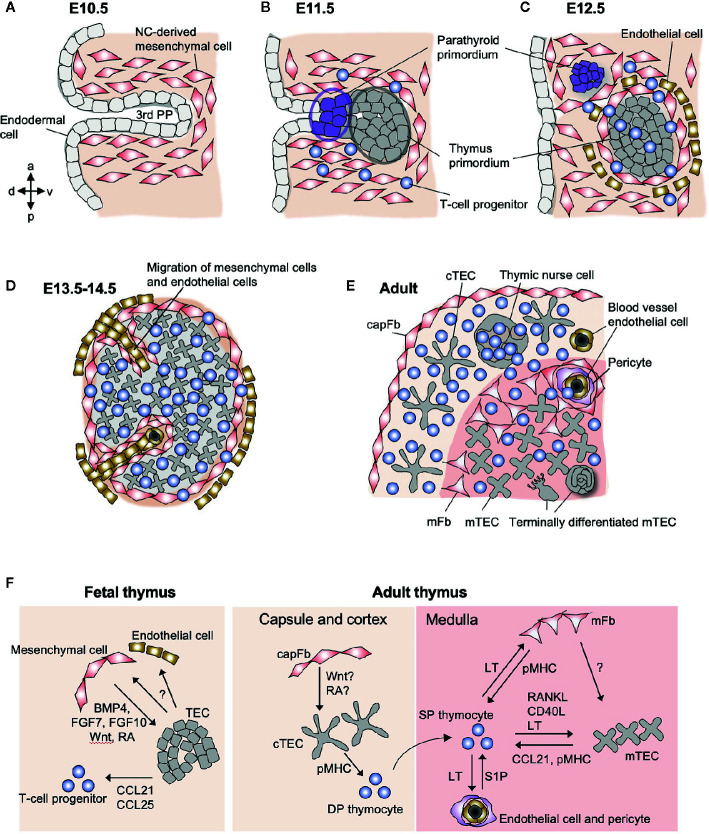
Figure 1.
Schematic representation of stromal cells in the fetal and adult thymus. (A) The third pharyngeal pouch (PP) is a structure temporary formed in the E9.5–10.5 embryo, whose patterning is regulated by the surrounding NC-derived mesenchymal cells. (B) On E11.5, endoderm-derived epithelial cells form primordia of parathyroid gland and thymus. (C) Both primordia separate from the foregut on E12.5, being surrounded by NC-derived mesenchymal cells and mesoderm-derived endothelial cells. From E11.5 to E12.5, T-cell progenitors migrate into the thymic primordium by the coordinating action of chemokines, Ccl21 produced by parathyroid epithelium and Ccl25 produced by thymic epithelium. (D) On E13.5, endothelial cells and mesenchymal cells begin to migrate into the thymic primordium to form vascular network. (E) The intrathymic mesenchymal cells differentiate to reticular mFbs and blood vessel pericytes, while the perithymic mesenchymal cells remain outside of the epithelium and form the thymic capsule. (F) Interactions among stromal cells and developing T cells in fetal and adult thymus. In fetal thymus, NC-derived mesenchymal cells produce BMP4, FGF7, FGF10, Wnt ligands, and retinoic acid (RA) to promote the differentiation and proliferation of TECs. Fetal TECs induce inward migration of mesenchymal cells and endothelial cells via unknown mechanism. In adult thymus, mFbs control mTEC development via yet unidentified factors, suggesting that mFbs lie upstream in the hierarchy of stromal interaction in the medulla. The development of mature mFbs with unique gene expression is controlled by lymphotoxin (LT) signals provided by SP thymocytes. SP thymocytes also produce RANKL and CD40L as well as LT to induce differentiation and proliferation of mTECs. Both mFbs and mTECs contribute to the production of self-antigens for the induction of T cell tolerance. mTECs produce CCL21 to attract positively selected SP thymocytes from the cortex to the medulla. The emigration of mature T cells from the thymus is promoted by S1P produced by blood vessel pericytes.