Figure 3.
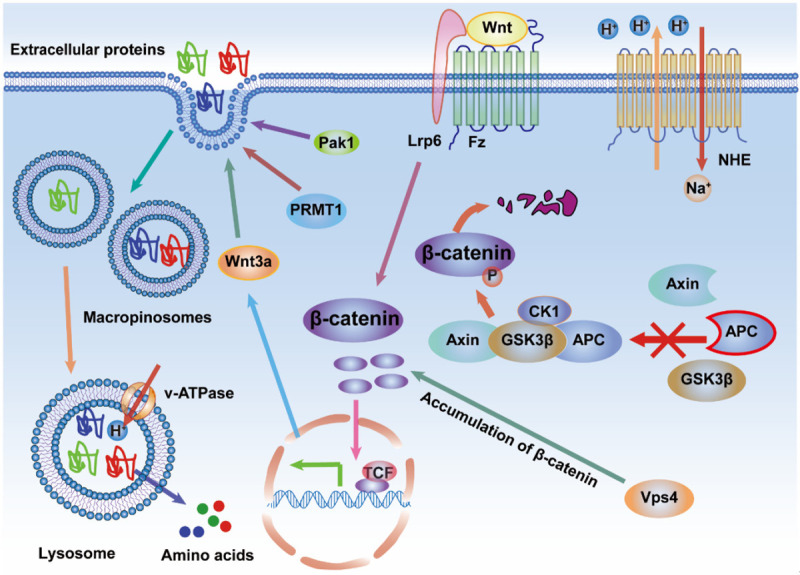
The Wnt growth factor triggers macropinocytosis by binding to co-receptors Frizzled (Fz) and LDL receptor-related protein 6 (Lrp6) on the cell surface. The stabilized upstream effector, β-catenin, can translocate into the nucleus and bind with TCF transcriptional factors to promote the expression of the downstream effector, Wnt3a, which can increase the uptake of extracellular proteins. The stabilization of β-catenin benefits from the functional incapacitation of the complex components, APC, Axin1, GSK3β, and CK1, that could destruct β-catenin. The vacuolar protein sorting 4 (Vps4) contributes to β-catenin accumulation in cancer cells. In addition, Wnt-driven macropinocytosis may require the protein arginine methyltransferase 1 (PRMT1) and Pak1 in cancer cells. However, the upstream effectors of PRMT1 and Pak1 in Wnt signaling pathway, are still unclear.
