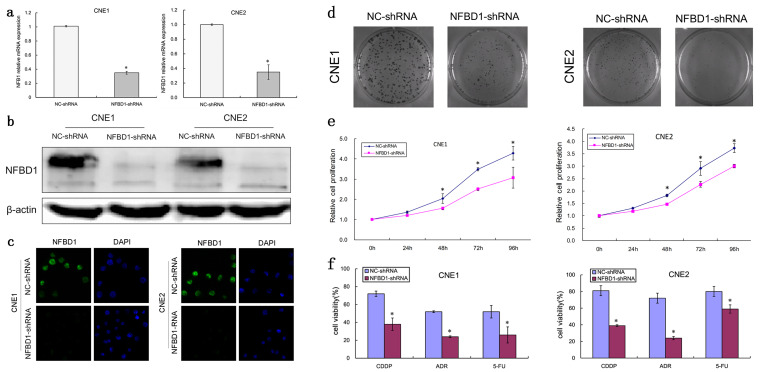
Figure 2.
NFBD1 depletion suppresses the proliferation of NPC cells and enhances their sensitivity to chemotherapeutic agents. Lentiviruses expressing NFBD1 shRNA and control shRNA were transfected into CNE1 cells. Transfected cells that stably expressed NFBD1 shRNA and NC-shRNA were obtained under puromycin (1 μg/ml) selection. (a) The effects of the lentivirus on the expression of NFBD1 mRNA were determined by qRT-PCR. The relative expression level of NFBD1 mRNA was significantly downregulated in the NFBD1-shRNA group. *p < 0.01 compared with the NC-shRNA group. The effects of lentiviral infection on the expression of NFBD1 protein were determined by Western blotting (b) and immunofluorescence (c). (d) Colony formation assay for NPC cells. Cells were cultured for 14 days, and the surviving colonies were stained and counted. (e) Growth curves of CNE1 and CNE2 cells. A CCK-8 assay was performed, and absorbance values at 450 nm were recorded from 0 to 96 h after the cells were seeded. (f) The depletion of NFBD1 enhances the sensitivity of NPC cells to ADR (0.2 μg/ml), CDDP (0.2 μg/ml), and 5-FU (0.4 μg/ml). Cell viability was examined using a CCK-8 assay. *p < 0.05.