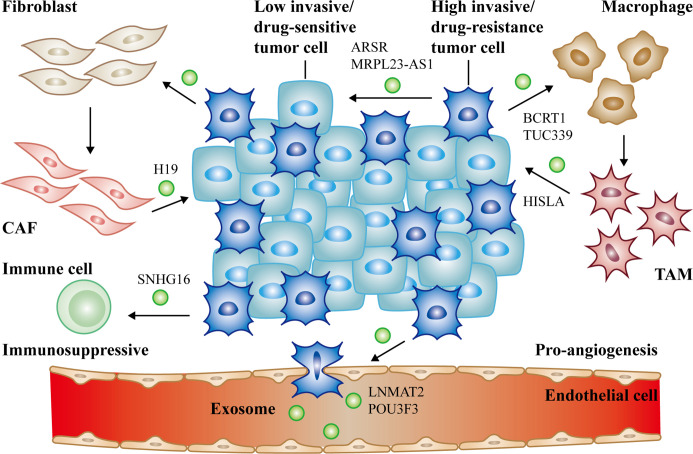
Figure 2.
The communication of exosomal long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) between cancer cells and non-cancer cells in tumor microenvironment. Cancer cells derived exosomal lncRNAs active fibroblasts, macrophages (lncRNA BCRT1, lncRNA TUC339), endothelial cells (lncRNA LNMAT2, lncRNA POU3F3) and suppress immune cells to form the PMN (lncRNA SNHG16). Reciprocally, activated CAFs (lncRNA H19), TAMs (lncRNA HISLA) can also deliver exosomal lncRNAs to promote cancer progression. Moreover, high/low invasive or drug-resistance/sensitive tumor cells can communicate with each other via exosomal lncRNAs as well (lncRNA ARSR, lncRNA MRPL23-AS1). All of the above together promote tumor growth, metastasis, and chemoresistance.