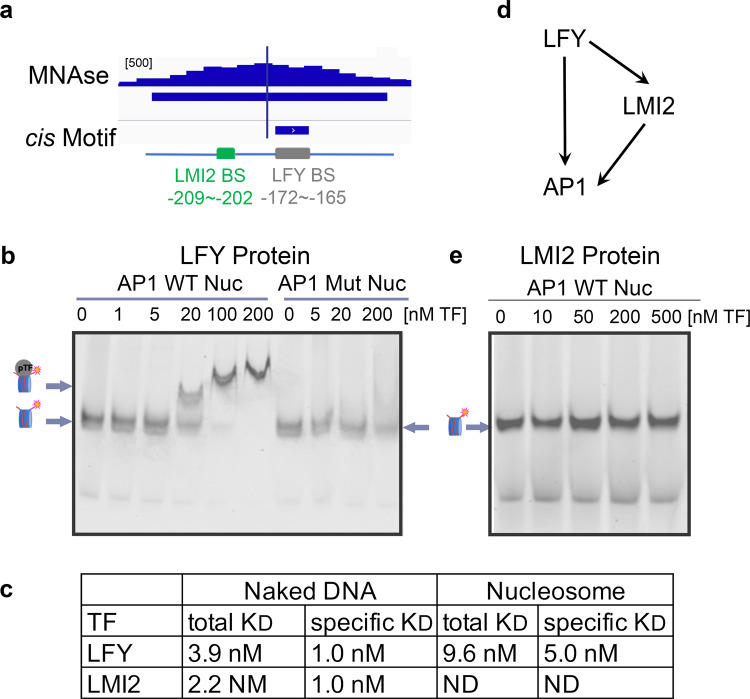
Fig. 1. The helix-turn-helix transcription factor LFY binds specifically and with high affinity to nucleosomal DNA in vitro.
a Top: Nucleosome at the AP1 regulatory region positioned over a functionally important LFY binding site53, 55. Vertical line: nucleosome mid-point (dyad). Browser screenshot: MNase-seq reads. Below: significant nucleosome (DANPOS q value ≤ 10−100) with color saturation proportional to the signal strength. Short horizontal line: LFY binding motif (consensus core = CCANTGG)53, 54, 57. Bottom: AP1 locus regulatory region with binding site for LFY and for the MYB transcription factor LMI251, 60 and their distance from the transcription start site. b EMSA of LFY binding to native AP1 regulatory DNA assembled into nucleosomes containing a wild-type (left) or a mutated (right) binding motif at the nucleosome dyad. Arrows and drawings on the left indicate nucleosome alone (bottom) and transcription factor nucleosome complex (top). The supershift observed at high molar excess is typical of nucleosomal EMSAs14, 15. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results. c Apparent dissociation constants (KD in nM) of LFY and LMI2 binding based on the decrement of nucleosome (total binding) or the first bound nucleosome (specific binding) as described in Ref. 14. ND: not detectable. d LFY and LMI2 feed-forward loop for transcriptional activation of AP151. e EMSA of LMI2 binding to native AP1 regulatory DNA containing the wild-type binding motif assembled into a nucleosome. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results. See also Supplementary Fig. 1.