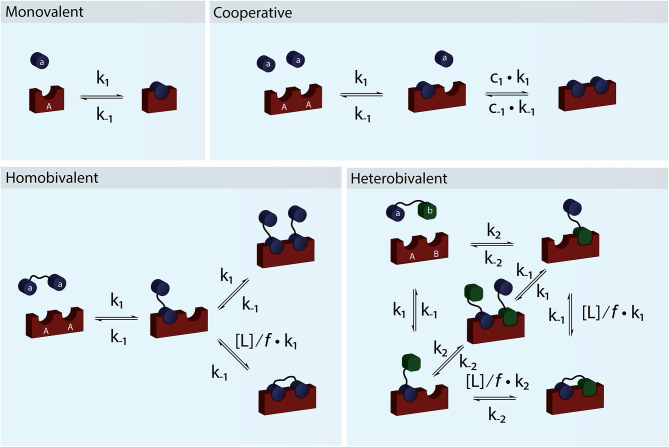
Figure 1.
Schematic figure showing monovalent, cooperative and homo- and heterobivalent reactions. In cooperative binding either one or both the association and dissociation rates of the second binding step may be modulated by cooperativity factors c1 and c−1. Only cases where only one of the interacting species are multitopic and where the reaction is not diffusion limited allows for accurate determination of the cooperativity. In multivalent binding, both of the interacting species are multitopic. For simplicity we have presented reaction schemes for both a homo- and heterobivalent interactions. In these cases the association rate of the second binding step is modulated by the local concentration, [L], and an empirical penalty factor, f. Multivalent interactions can also be cooperative but the direct effect is difficult to determine accurately.