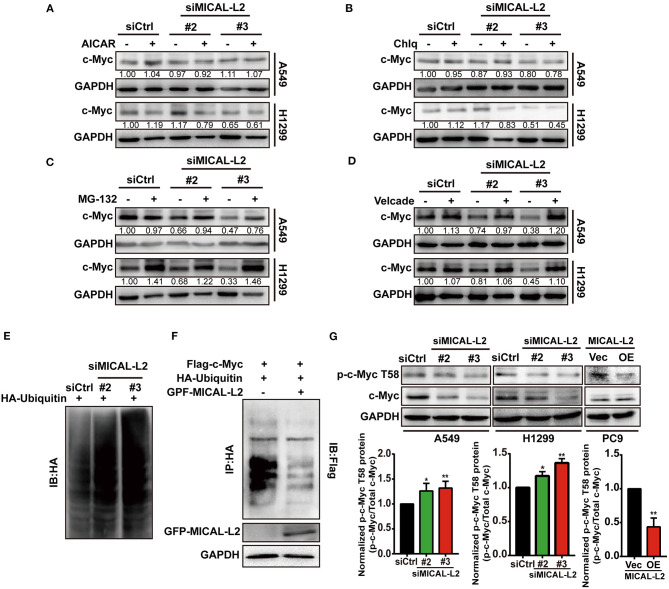
Figure 7.
MICAL-L2 inhibited c-Myc ubiquitin-mediated degradation. (A–D) A549 and H1299 cells transfected with small interfering (si) RNA targeting MICAL-L2 (siMICAL-L2) were treated with AICAR (0.2 mM), chloroquine (10 μM), MG-132 (20 μM), and Velcade (10 μM) for 24 h. Total proteins were then extracted from the lysates and subjected to Western blotting to detect the expression of c-Myc. GAPDH served as the loading control. (E) H1299 cells were transfected with HA-ubiquitin and siMICAL-L2 and c-Myc polyubiquitination was detected by Western blotting using the indicated antibodies. (F) H1299 cells were co-transfected with HA-ubiquitin and GFP-MICAL-L2, Flag-c-Myc, or empty vector, following which c-Myc polyubiquitination was assayed. (G) A549 and H1299 cells were transfected with control siRNA or siMICAL-2. Total proteins were then extracted and analyzed for the expression of phosphorylated-c-Myc (T58) by Western blotting. PC9 cells were transfected with empty vector or MICAL-L2 expression plasmids. Total proteins were then extracted and analyzed for the expression of phosphorylated-c-Myc (T58) by Western blotting. Western blotting bands corresponding to phosphorylated-c-Myc/c-Myc were quantified and normalized against GAPDH. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 relative to control cells.