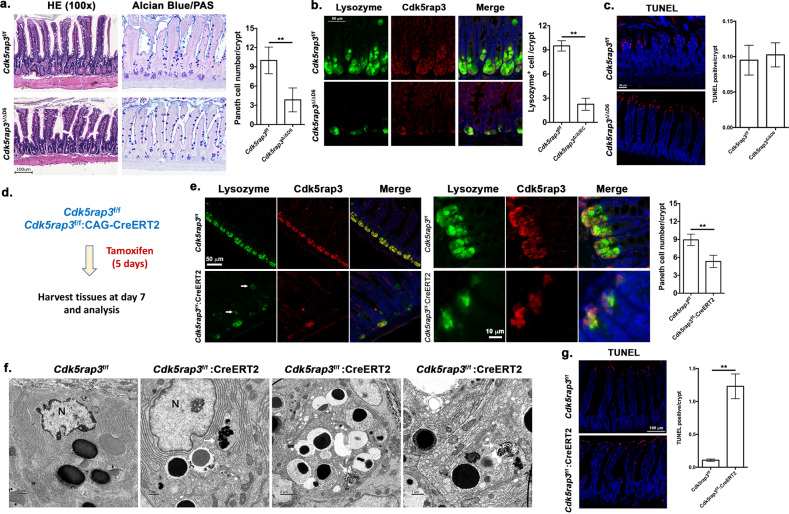
Fig. 3. Paneth cell-specific deletion of Cdk5rap3 causes loss of Paneth cell.
a H&E and Alcian blue/PAS staining of ileal sections of wild-type and Cdk5rap3 Paneth cell-specific Cdk5rap3 KO mice (Cdk5rap3∆/∆D6). The number of Paneth cells per crypt was scored. **p < 0.01. (n = 4 mice per genotype). b Lysozyme staining of ileal sections of wild-type and Cdkrap3∆/∆D6 mice. Lysozyme-positive cells per crypt were scored. **p < 0.01. (n = 4 mice per genotype). c TUNEL staining of ileal sections of wild-type and Cdkrap3∆/∆D6 mice. TUNEL positive cells per crypt were scored (n = 4 mice per genotype). d Experimental procedure to analyze the effect of acute deletion of Cdk5rap3. Mice were treated with daily i.p. injection of tamoxifen (75 mg/kg) for 5 consecutive days, and the tissues were harvested at day 7 for fixation and analysis. e Lysozyme staining of ileal sections of wild-type and Cdkrap3 deficient mice. Lysozyme-positive cells per crypt were scored. **p < 0.01. (n = 4 mice per genotype). f TEM analysis of the crypts of wild-type and Cdkrap3 deficient small intestine. The nucleus was labeled as “N”, and autolysosomes were marked by white arrows. g TUNEL staining of ileal sections of wild-type and Cdkrap3 deficient mice. TUNEL positive cells per crypt were scored. **p < 0.01. (n = 4 mice per genotype).