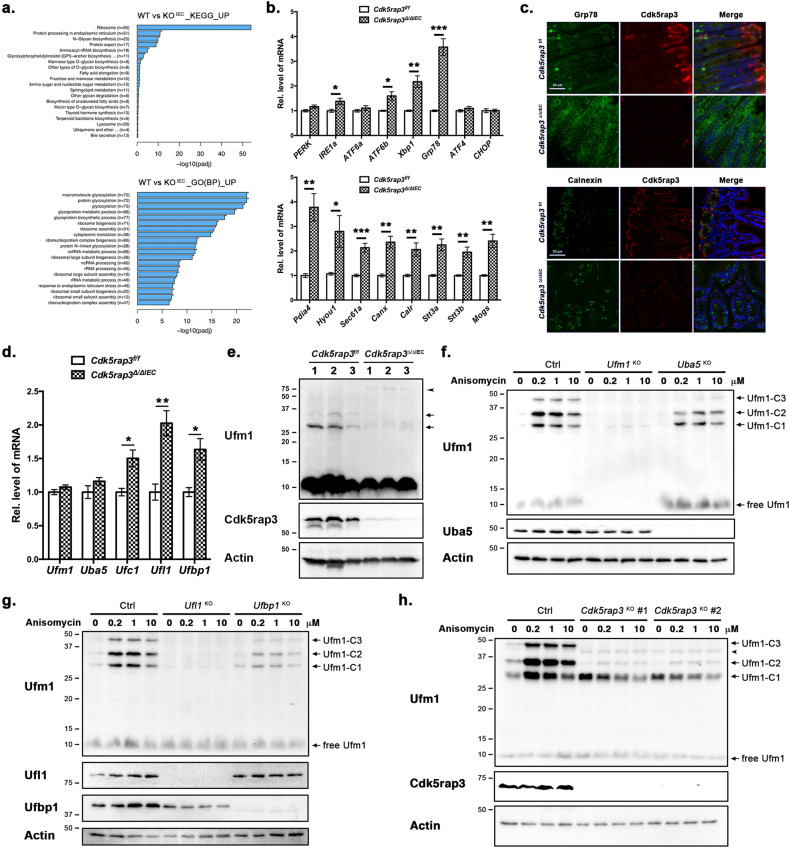
Fig. 5. Cdk5rap3 knockout results in defective ufmylation pathway and activation of Unfolded Protein Response (UPR).
a GO and KEGG enrichment analysis of up-regulated DEGs in Cdkrap3∆/∆IEC intestine. b Quantitative RT-PCR confirmation of up-regulated genes that are involved in UPR and ER-related protein glycosylation and folding. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 (n = 4 mice per genotype). c Immunofluorescence staining of Grp78/Bip and Calnexin in ileal section of wild-type and Cdkrap3∆/∆IEC mice. d Up-regulation of the components of the Ufm1 conjugation system induced by Cdk5rap3 knockout. Total RNA was isolated from small intestinal scrapes. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01 (n = 4 mice per genotype). e The Ufm1 conjugates in wild-type and Cdk5rap3 KO IECs. Cell lysates of isolated crypts were subjected to immunoblotting of Ufm1. Endogenous of Ufm1 conjugates in wild-type cells were marked by arrows, while a new Ufm1 conjugate in Cdk5rap3 KO cells was indicated by an arrowhead. f UFMylation in wild-type, Ufm1 KO and Uba5 KO 293 T cells in the absence and presence of anisomycin. Cells were treated with anisomycin for 1 h. Ufm1-C1, 2, 3 are endogenous Ufm1 conjugates. g UFMylation in wild-type, Ufl1 KO and Ufbp1 KO 293T cells with and without anisomycin. h UFMylation in wild-type and Cdk5rap3 KO 293T cells with and without anisomycin. A new Ufm1 conjugate in Cdk5rap3 KO cells was indicated by an arrowhead (around 45 kD).