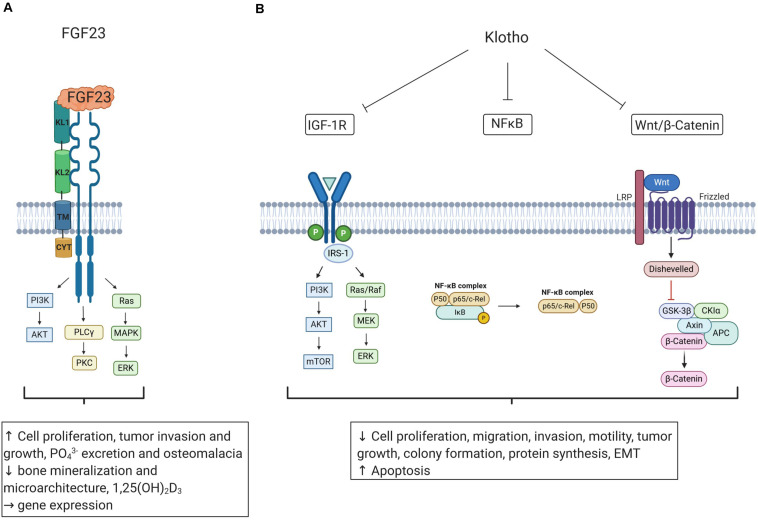
FIGURE 2.
The influence of FGF23 and Klotho on oncogenic and tumor-suppressing pathways. (A) FGF23 binds to FGFRs and coreceptor KL and may impact cell proliferation, tumor growth, and bone gene transcription. Tumor-induced elevation of FGF23 production may cause phosphate wasting, 1,25(OH)2D3 reduction, and osteomalacia. (B) Klotho (KL) is a tumor-suppressor inhibiting pathways relevant for tumorigenesis including IGF-1R, Wnt/β-catenin, and NF-κB signaling, resulting in decreased cell proliferation, invasion, migration, tumor growth, protein synthesis, and EMT and inducing apoptosis. Figure according to Sachdeva et al. (2020). Created with BioRender.com. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R); phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K); mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR); mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK); mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase (MEK); extracellular receptor signal-related kinase (ERK); insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1); nuclear factor ‘kappa-light-chain-enhancer’ of activated B-cells (NF-κB); iκappaB kinase (IκB); low density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP); glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β); adenomatous polyposis coli (APC); phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ), protein kinase C (PKC); epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT); phosphate (PO43−), 1,25(OH)2D3 (active vitamin D).