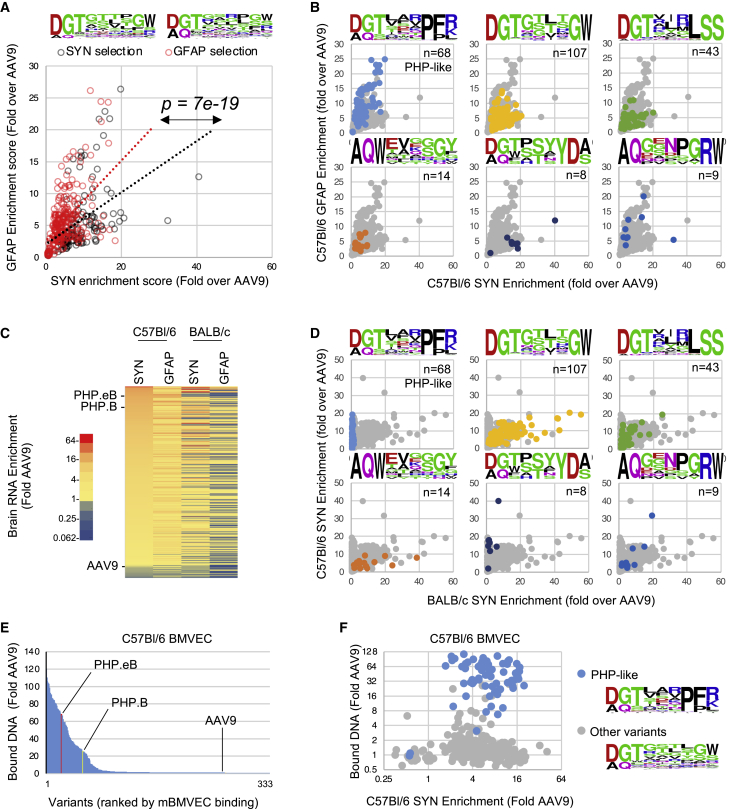
Figure 3.
Genotype-to-phenotype analysis of synthetic capsid pool from C57BL/6 CNS biopanning
(A) Comparative neuron and astrocyte fitness of the capsid variants originating from SYN- or GFAP-driven library biopanning (black and red circles, respectively). Each data point represents the average neuron (SYN-driven) and astrocyte (GFAP-driven) RNA enrichment score in i.v.-dosed C57BL/6 mice (n = 6), normalized to AAV9. Linear regression trendline of each population is indicated. p value indicates the statistical difference between the average GFAP-to-SYN score ratio of each subpopulation (unpaired t test). Frequency plots of peptides from SYN- and GFAP-evolved subpools are indicated on top. (B) Enrichment scores of each capsid sequence family in GFAP- (y axis) and SYN-driven RNA assays (x axis). The frequency plots and number of variants in each group are indicated. (C) Comparative brain RNA enrichment of 330 variants in C57BL/6 mice (n = 6) and BALB/c mice (n = 6) following i.v. injection. Color scale indicates the average RNA enrichment score normalized to AAV9. Variants are ranked by SYN-driven RNA enrichment score in C57BL/6 mice. (D) Comparative SYN-driven RNA enrichment score of distinct capsid families in C57BL/6 and BALB/c mice. The frequency plots and number of variants of each group are indicated. (E) Multiplexed binding assay of synthetic capsid pool to C57BL/6 mouse primary brain microvascular endothelial cells (BMVECs). Values indicate bound viral DNA enrichment score relative to AAV9. Ranking of reference PHP.eB, PHP.B, and AAV9 capsids is indicated. (F) Scatterplot presenting the correlation between virus binding to mouse BMVECs and C57BL/6 brain RNA enrichment scores. The PHP-like capsid variants are indicated by blue dots, all other variants by gray dots.