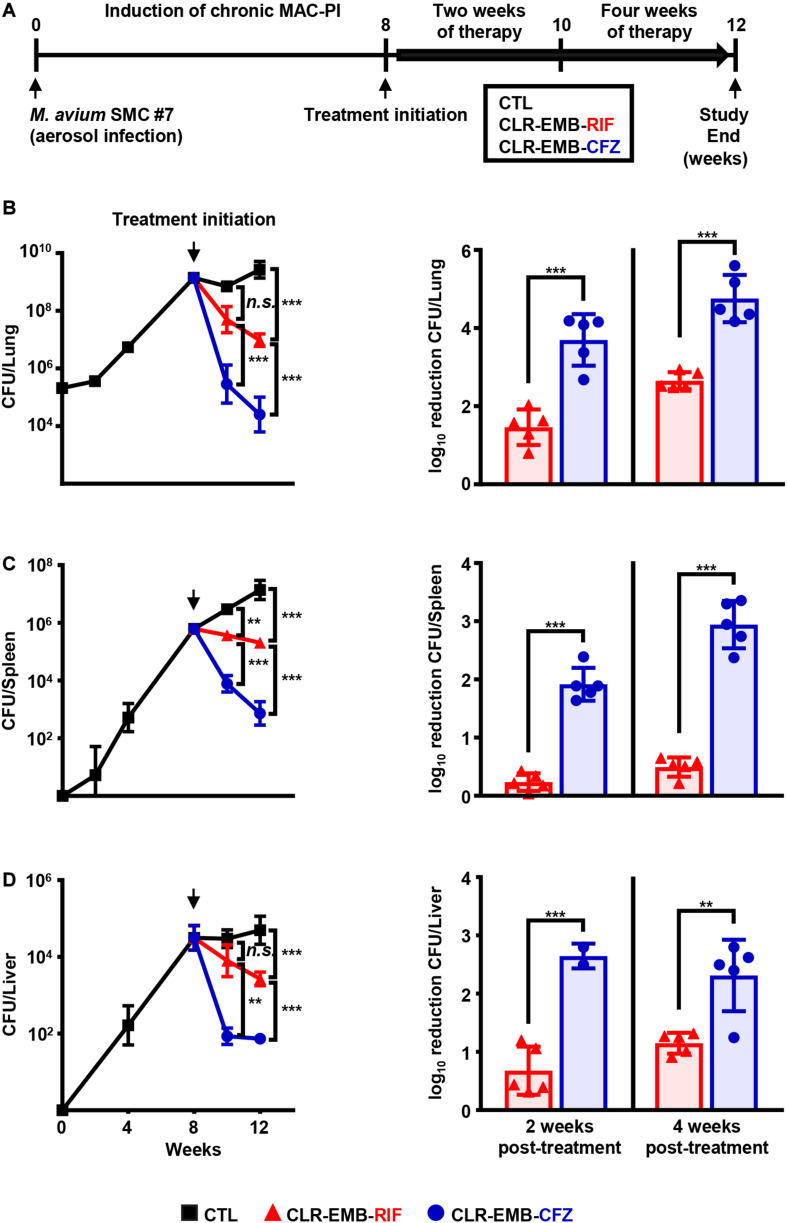
FIGURE 4.
Comparative assessment of treatment efficacy of the standard and CFZ-containing regimens in a murine model of chronic progressive MAC-PI. (A) Schematic design of the in vivo experiment. BALB/c mice were infected with the M. avium SMC #7 clinical isolate via aerosolization, achieving a mean initial bacterial number of 2 × 105 CFUs in the lungs. Two weeks and 4 weeks of therapy were initiated with the standard and CFZ-containing regimens at 8 weeks post-infection. The daily drug doses were 100 mg/kg for CLR and EMB, 10 mg/kg for RIF and 20 mg/kg for CFZ. The mice were euthanized, and the lungs were homogenized for histopathological examination and bacterial counts at 2 and 4 weeks post-treatment. Plotted infection data and mean CFU counts and bar graphs for the log10 reduction in CFU from treatment initiation in the (B) lungs, (C) spleens and (D) livers were assessed after 2 and 4 weeks of treatment with the two regimens by plating serially diluted tissue lysates onto 7H10-OADC agar plates. The broken vertical line of each plotted data indicates the day of treatment initiation. The statistical significance in (B–D) was calculated by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple comparison test, and the results are represented as the mean value ± S.D. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 and n.s., not significant. MAC-PI, M. avium complex-pulmonary infection; CTL, untreated control; CLR-EMB-RIF, standard regimen; CLR-EMB-CFZ, CFZ-containing regimen.