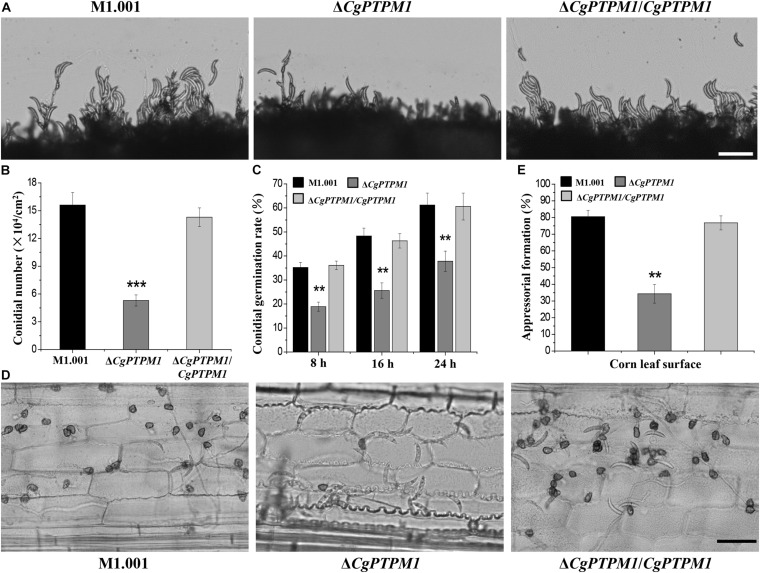
FIGURE 3.
CgPTPM1 is related to conidiation, conidial germination and the formation of appressoria. (A) Observation of conidiation. Conidia of wild type M1.001, the mutant ΔCgPTPM1 and complementation strain ΔCgPTPM1/CgPTPM1 from 14-day-old potato dextrose agar (PDA) media were transferred to glass slides and observed under an optical microscope. (B) Statistical analysis of the conidiation of strains cultured on PDA plates for 14 days. (C) Statistical analysis of conidial germination rates of strains on epidermal cells of corn leaves at 8, 16, and 24 h post infection (hpi). Conidial germination was measured at a concentration of 1 × 105 conidia/mL, and more than 200 conidia were identified in each experiment. (D) Observation of the formation of appressoria on epidermal cells of corn leaves. A conidial suspension of 1 × 105 conidia/mL was used to inoculate the corn leaf epidermal cells, and the formation of appressoria was observed at 24 hpi. (E) Statistical analysis of the rates of formation of appressoria of strains on corn leaf epidermal cells at 24 hpi. More than 200 appressoria in the experiment were identified. Error bars represent ± SD of three independent repeated samples. Two asterisks (**) represent an extremely significant difference at 0.001 < P < 0.01, and three asterisks (***) represent an extremely significant differences at P < 0.001. Scale bar = 50 μm.