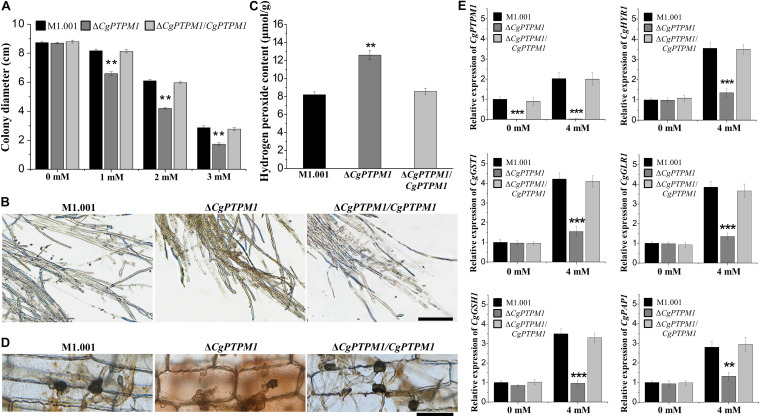
FIGURE 5.
The mutant ΔCgPTPM1 is more sensitive to H2O2 and cannot scavenge excessive H2O2 in a timely manner. (A) Statistical analysis of the colony diameters of wild type, mutant and complementation strains on complete minimal media (CM) plates that contain H2O2. (B) The results of 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) staining of vegetative hyphae after three types of strains were cultured on CM plates for 4 days. (C) Determination of the concentration of H2O2 in the wild type, mutant and complementation strains. (D) DAB staining of the excised leaves of corn infected by the wild type, ΔCgPTPM1 and complementation strains at 48 h post infection. (E) The expression of CgPTPM1 could affect the expression of antioxidant gene orthologs in C. graminicola. Compared with the 0 mM H2O2 treatment, the expression of CgPTPM1 in wild type and complementation strains increased when induced with 4 mM H2O2, and the expression of the other five antioxidant-related genes CgHYR1, CgGST1, CgGLR1, CgGSH1 and CgPAP1 was upregulated. In the mutant, CgPTPM1 was not expressed, and the expression of the other five genes did not change significantly. Two asterisks (**) represent an extremely significant difference at 0.001 < P < 0.01, and three asterisks (***) represent an extremely significant differences at P < 0.001. Error bars represent ± SD of three independent repeated samples. Scale bar = 20 μm.