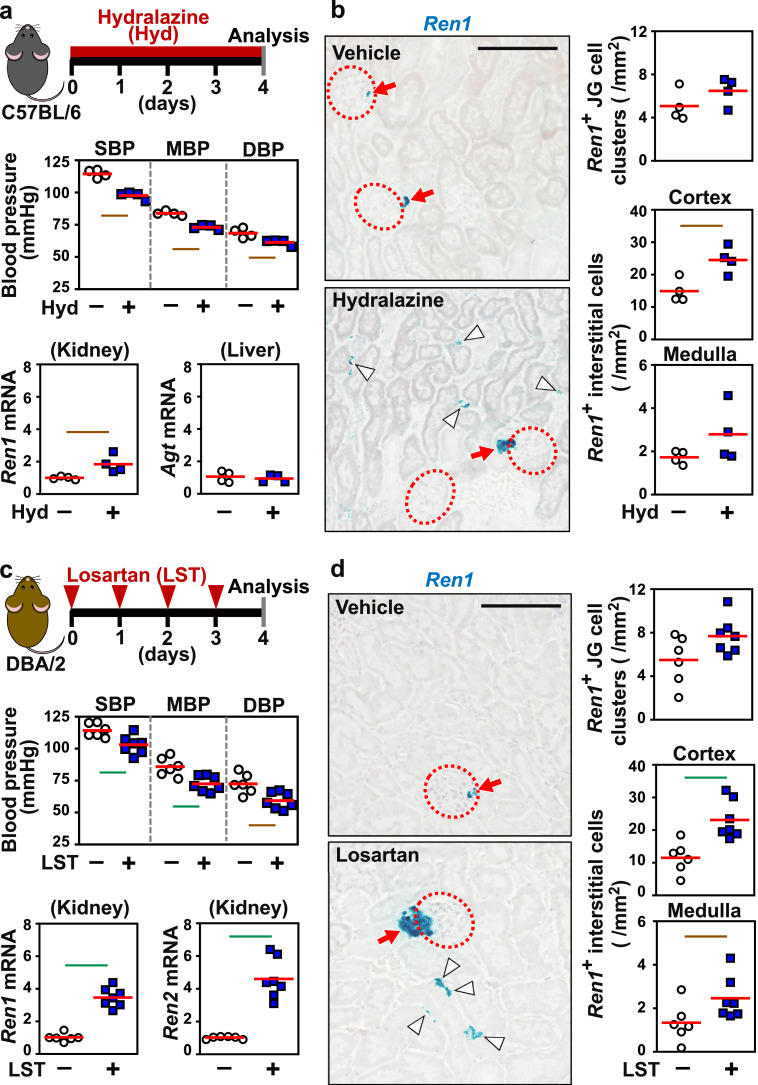
Fig. 6.
Renal interstitial renin is induced by antihypertensive agents. (a) Vasodilator (hydralazine, Hyd) administration causes hypotension and renal renin induction in wild-type C56BL/6 mice. The experimental scheme, blood pressure, Ren1 mRNA levels in kidney, and Agt mRNA levels in liver are shown. (b) Representative images and quantification of ISH of Ren1 mRNA in kidney sections of mice freely drinking Hyd for 4 days. (c) Injection of an AngII receptor blocker reagent (losartan, LST) into wild-type DBA/2 mice resulted in hypotension and the induction of the genes encoding renin (Ren1 and Ren2). The experimental scheme, blood pressure, and Ren1 and Ren2 mRNA levels in the kidney are shown. (d) Representative images and quantification of ISH of Ren1 mRNA in kidney sections of mice after LST administration. The average expression levels (red bars) in the control mice were set as 1 for each gene expression analysis (a and c). n = 4–7 per group. Dotted circles and red arrows indicate glomeruli and JG cells, respectively (b and d). White arrowheads indicate interstitial fibroblasts positive for Ren1 (blue in b and d). Scale bars represent 100 μm (b and d). Green and brown lines indicate P<0.01 and P<0.05, respectively, in the Wilcoxon-Mann-Whitney test. .