Figure 1.
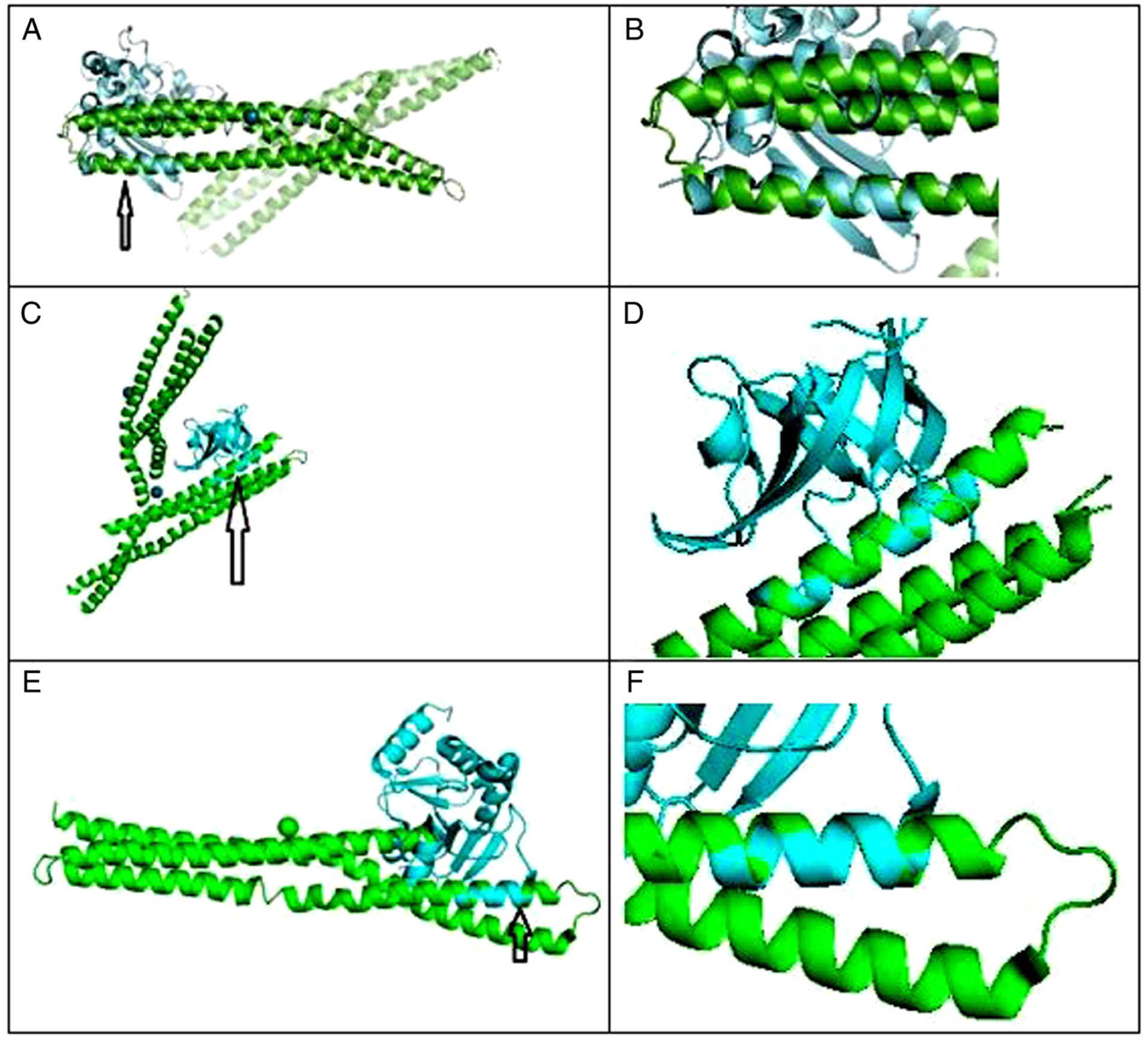
(A) C-terminal dimerization domain of nucleocapsid phosphoprotein from SARS-CoV2 aligned with BAR domain from human BIN1/amphiphysin II. Arrow points to closely aligned (RMSD=1.850Å) alpha helices of SARS-Cov2 (blue) and BIN1 (green). (B) Closeup of aligned α helices. Amino acid residues serine 81-tyrosine 100 of BIN1 aligned closely with residues asparagine 99-proline 118 of SARS-Cov2. (C) BAR domain from human BIN1/amphiphysin II (green) and SARS-CoV-2 NSP1 (blue); arrow points to closely aligned (RMSD=0.298 Å) α helices of SARS-Cov2 NSP1 and BIN1. Amino acid residues glutamic acid 229-asparagine 243 of BIN1 aligned closely with residues valine 26-glycine 40 of SARS-Cov2 NSP1. (D) Closeup view of closely aligned α helices in part C. (E) BAR domain from human BIN1/Amphiphysin II (green) and SARS-CoV-2 NSP3 (blue); arrow points to closely aligned (RMSD = 0.795 Å) α helices of SARS-Cov2 NSP3 and BIN1. Amino acid residues glutamic acid 168-valine 158 of BIN1 aligned closely with residues valine 267-arginine 277 of SARS-Cov2 NSP3. (F) Closeup view of closely aligned α helices in part E.
