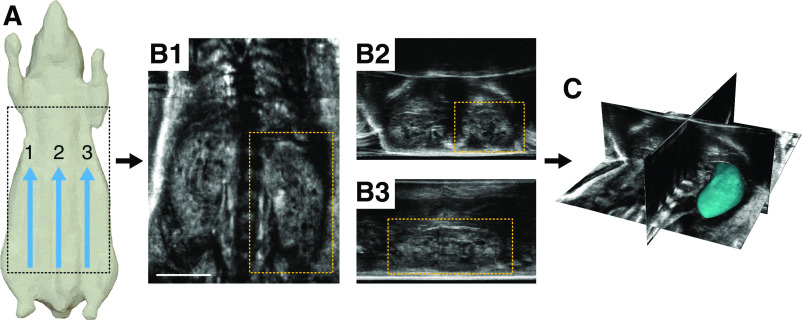
Figure 1.
An overview of the acquisition workflow for the robotic ultrasound system. (A) Multiple parallel sweeps are acquired, usually three, resulting in thousands of individual two-dimensional images from across the animal’s body. (B and C) These images are then stitched together to produce a single wide-field three-dimensional (3D) image volume, which can be viewed in different orientations. The 3D data can be seen in (B1) frontal, (B2) transverse, and (B3) sagittal planes, respectively. (C) Each kidney can then be segmented in 3D to assess total kidney volume. Scale bar, 1 cm.