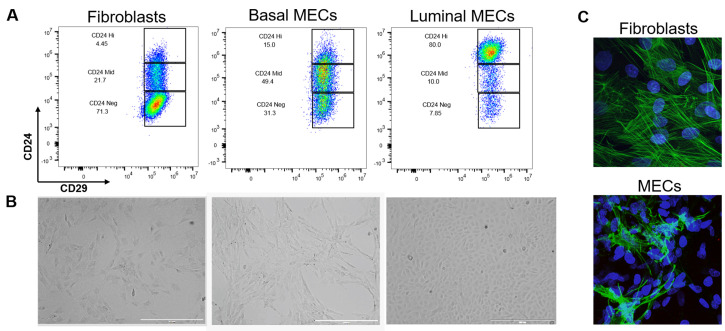
Figure 6. Separation and validation of fibroblasts, luminal, and basal MECs.
After 48 h in ULA, MECs were plated onto collagen coated plates in MEC media + Y-27632. When the culture was 80% confluent, luminal and basal cells were separated by differential trypsinization and plated as purified populations. Fibroblasts were selected by differential attachment after negative selection but before culturing in ULA plates. A. Immunophenotyping of fibroblasts and MECs by expression of CD24 and CD29. While CD29 expression is constant across all three cell lines, fibroblasts are CD24neg, basal cells CD24mid, and luminal cells CD24hi. B. 2D morphology of fibroblasts compared to basal and luminal cells plated on collagen. Brightfield images were taken at 4x on the EVOS, scale bars = 1,000 µm. Note the mesenchymal appearance of basal cells and the tightly packed cuboidal appearance of luminal cells. C. We used immunofluorescence as a final verification that our epithelial cultures do not contain fibroblasts (and vice versa that our fibroblast cultures do not contain epithelial contamination) by staining rat fibroblasts and negatively-selected MECS (pooled luminal and basal cells) with an anti-smooth muscle actin antibody (green) and DAPI (nuclear stain, blue). Fibroblasts have distinct actin stress fiber formation whereas positive basal cells in the MEC culture present with membranous smooth muscle actin. Z-stacks were acquired at 60x on a Nikon A1plus-RSi Laser Scanning confocal microscope. Maximum intensity projection images were generated using FIJI.