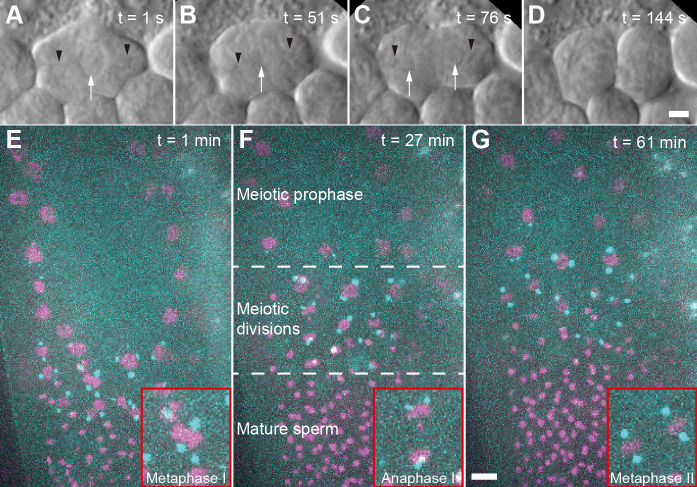
Figure 1. Imaging of C. elegans male germ cells.
A. DIC imaging of a primary spermatocyte dissected from a wild-type (Bristol N2) male. The cell is in prometaphase with chromosomes visible in the center of the cell. Black arrow heads indicating the approx. position of the centrosomes, white arrow indicates the chromosomes. B. Cell in metaphase I. C. Cell in anaphase I. D. Cell finishing first meiotic division. Scale bar for (A-D), 2 µm. E. Fluorescence image of an immobilized male (strain TMR17) after bleach correction. This image is a projection of 21 z-slices taken one minute after starting the data acquisition. Chromosomes labelled with histone H2B::mCherry are shown in magenta, spindle poles are labelled with γ-tubulin::GFP and shown in cyan. The inset (red frame) shows a metaphase I spindle. F. Projection of 24 z-slices, 27 min after starting the image acquisition. In this field-of-view, different regions of a gonad are shown. These regions include meiotic prophase, various meiotic divisions of in meiosis I and II, and mature sperm. The inset (red frame) shows an anaphase I spindle. G. Projection of 21 z-slices, 61 min after starting the image acquisition. The inset (red frame) shows two spindles in metaphase II, Scale bar for (E-G), 5 µm.