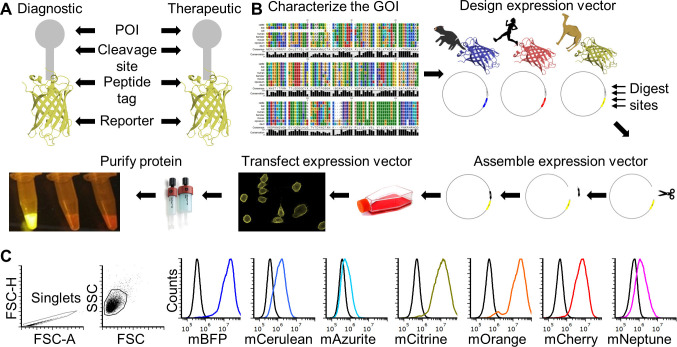
Figure 1. FAST protein schematic and initial testing.
A. Schematic diagram of FAST protein therapeutic and diagnostic (i.e., theranostic) features. B. Graphic overview of FAST protein system including key steps: (1) characterize gene-of-interest (GOI) in silico; (2) design expression vectors; (3) digest FAST base vectors and insert alternative GOIs or colors; (4) transfect expression vectors into mammalian cells and monitor using fluorescent microscopy or flow cytometry; (5) purify the protein using 6xHistidine tag, visualize fluorescent color to show protein is in-frame and correctly folded. Image of microfuge tubes shows 100 μl of mCitrine, mOrange, and mCherry FAST proteins (1 mg/ml) excited with blue light with amber filter. Full protocols for vector construction and protein testing are available in the Supplementary Materials. C. Results of flow cytometry binding assay using Tasmanian devil 41BB (aka TNFRSF9, CD137) FAST proteins and cell lines expressing 41BB ligand (aka TNFSF9, CD137L). The colored lines in the histograms show binding of devil 41BB fused to mTagBFP, mCerulean3, mAzurite, mCitrine, mOrange, mCherry, or mNeptune2 to Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells transfected with devil 41BBL, and the black lines show binding to untransfected CHO cells. Figure reprinted from Flies et al. (2020) under CC BY-NC license.