Figure 3.
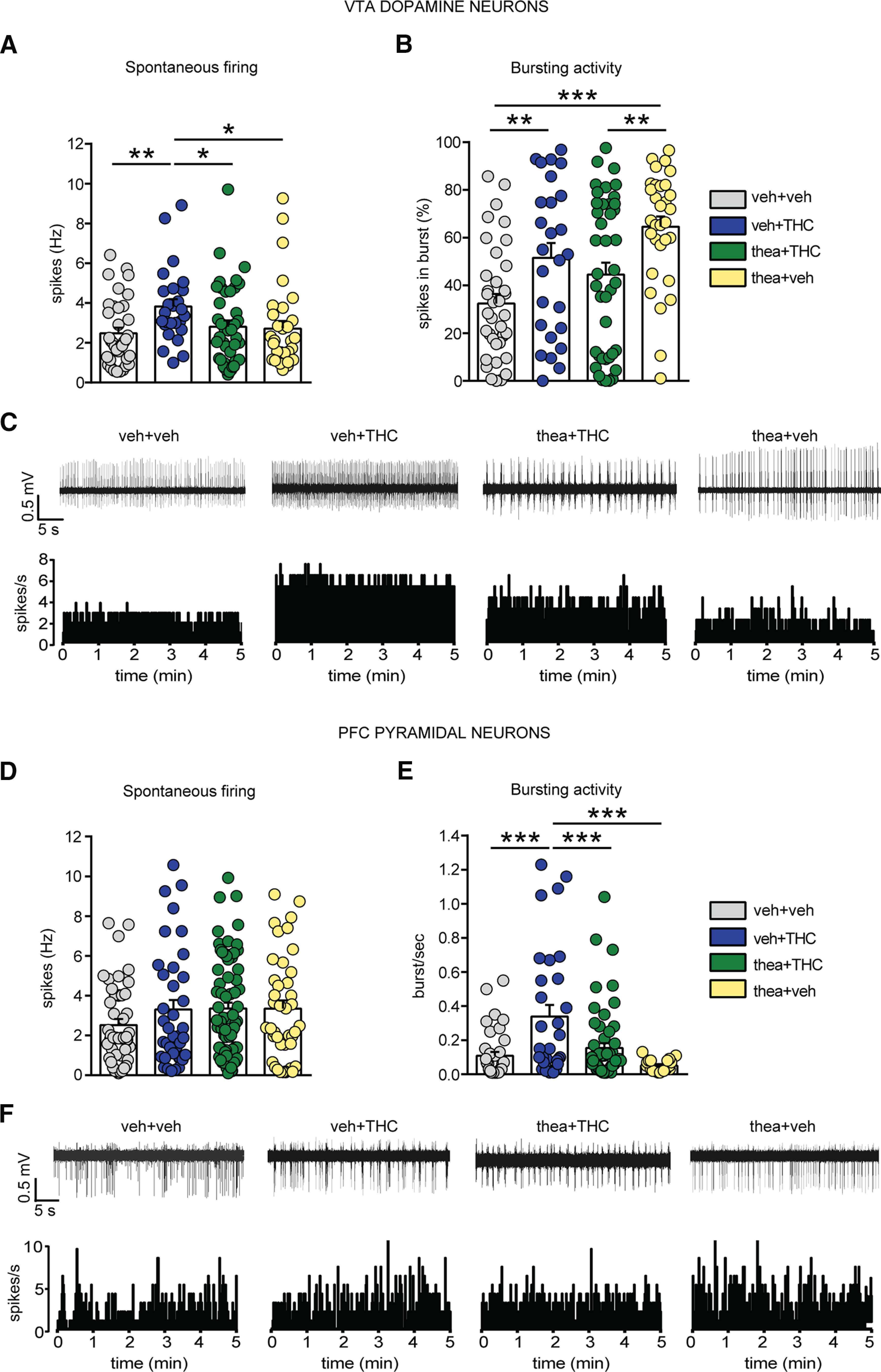
Effects of l-theanine exposure on adolescent THC-induced alterations of VTA DA and PFC pyramidal activity. A, l-Theanine prevents the subcortical hyperdopaminergic state induced by THC in terms of firing frequency. B, THC-treated rats exhibited an increase in bursting activity, which was not prevented by l-theanine + THC or l-theanine alone. Rats exposed to l-theanine alone showed a higher bursting activity when compared with the other groups (n = 36 cells from 6 vehicle rats; n = 26 cells from 5 THC rats; n = 41 cells from 4 thea + THC rats; n = 31 cells from 5 theanine rats; two-way ANCOVA, post hoc Fisher's LSD; *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001). C, Traces and rate histograms of representative VTA DA neurons recorded from each group. D, The firing rate of spontaneous PFC putative pyramidal neurons was not altered by adolescent THC treatment (n = 45 cells from 7 vehicle rats; n = 37 cells from 5 THC rats; n = 74 cells from 6 thea + THC rats; n = 40 cells from 5 theanine rats; two-way ANCOVA, post hoc Fisher's LSD; p > 0.05). E, However, the analysis of bursting activity revealed that l-theanine significantly prevented hyperbursting phenotypes induced by adolescent THC (n = 37 cells from 7 vehicle rats; n = 31 cells from 5 THC rats; n = 57 cells from 6 thea + THC rats; n = 20 cells from 5 theanine rats; two-way ANCOVA, post hoc Fisher's LSD; ***p < 0.001). F, Traces and rate histograms of representative PFC pyramidal neurons recorded from each group.
