Figure 8.
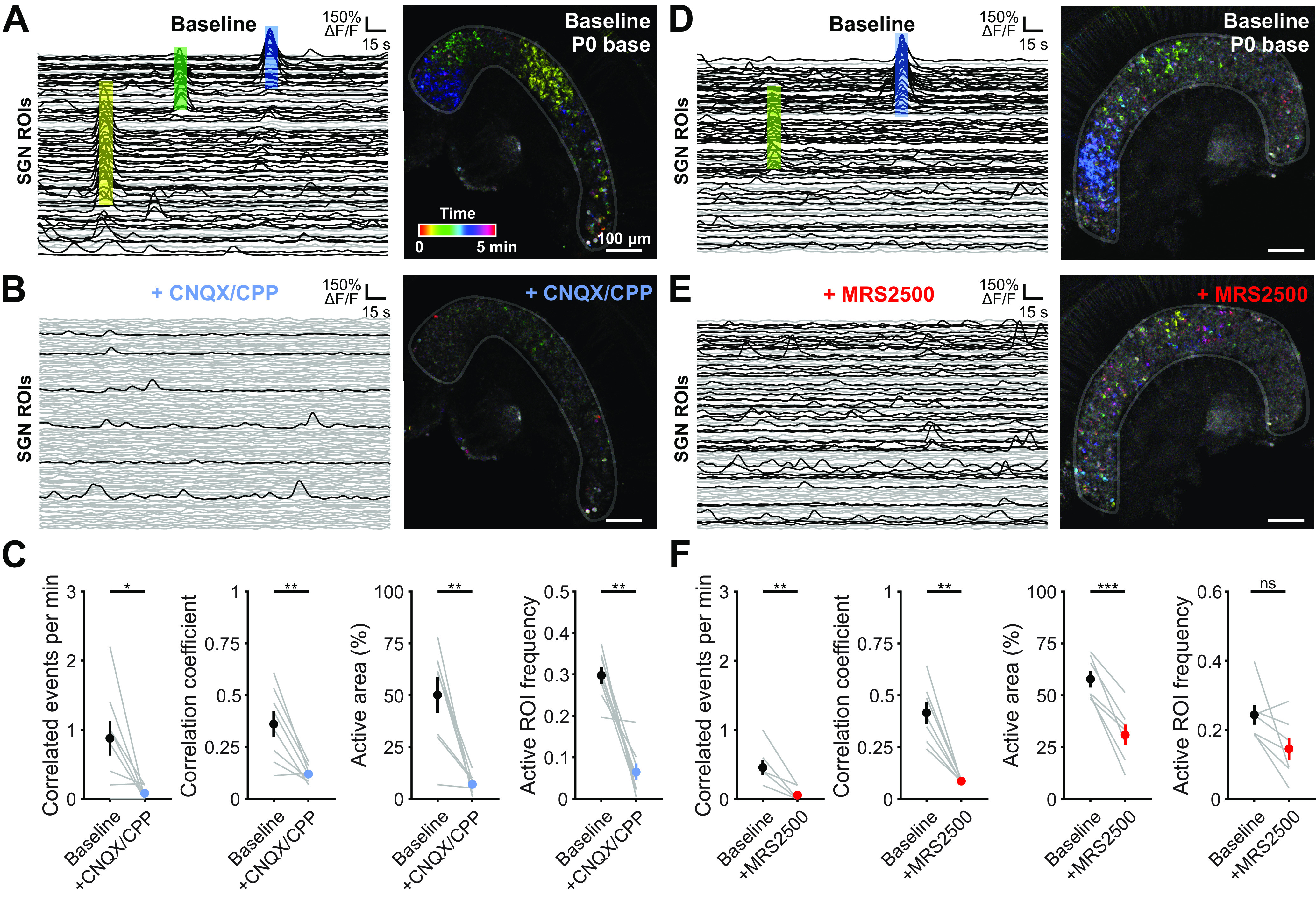
Correlated activation of SGNs requires P2ry1-mediated excitation of IHCs. A, Individual ROI traces and time-color representation of Ca2+ transients in control (baseline) conditions from the basal turn of cochlea isolated from a P0 Snap25-T2A-GCaMP6s mouse. Colored boxes on left correspond to same colored events on right. Black traces represent ROIs with at least one detected peak (fifth percentile value ± 5 SDs). Gray traces represent ROIs with no detected peaks. B, Similar to A, but with application of the AMPAR and NMDAR antagonists CNQX (50 μm) and CPP (100 μm). C, Quantification of correlated event frequency, correlation coefficient (80th percentile), active area (percentage of ROIs with at least one detected peak), and frequency of transients in active ROIs before and after application of CNQX/CPP. n = 8 P0 basal portions from 4 mice. **p < 0.005; *p < 0.05; paired t test with Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment. D, Similar to A. E, Similar to D, but with bath application of P2RY1 antagonist (MRS2500, 1 μm). F, Quantification of correlated event frequency, correlation coefficient (80th percentile), active area (percentage of ROIs with at least one detected peak), and frequency of transients in active ROIs before and application of MRS2500. n = 7 P0 basal portions from 4 mice. ***p < 5e-4; **p < 0.005; *p < 0.05; paired t test with Benjamini-Hochberg adjustment.
