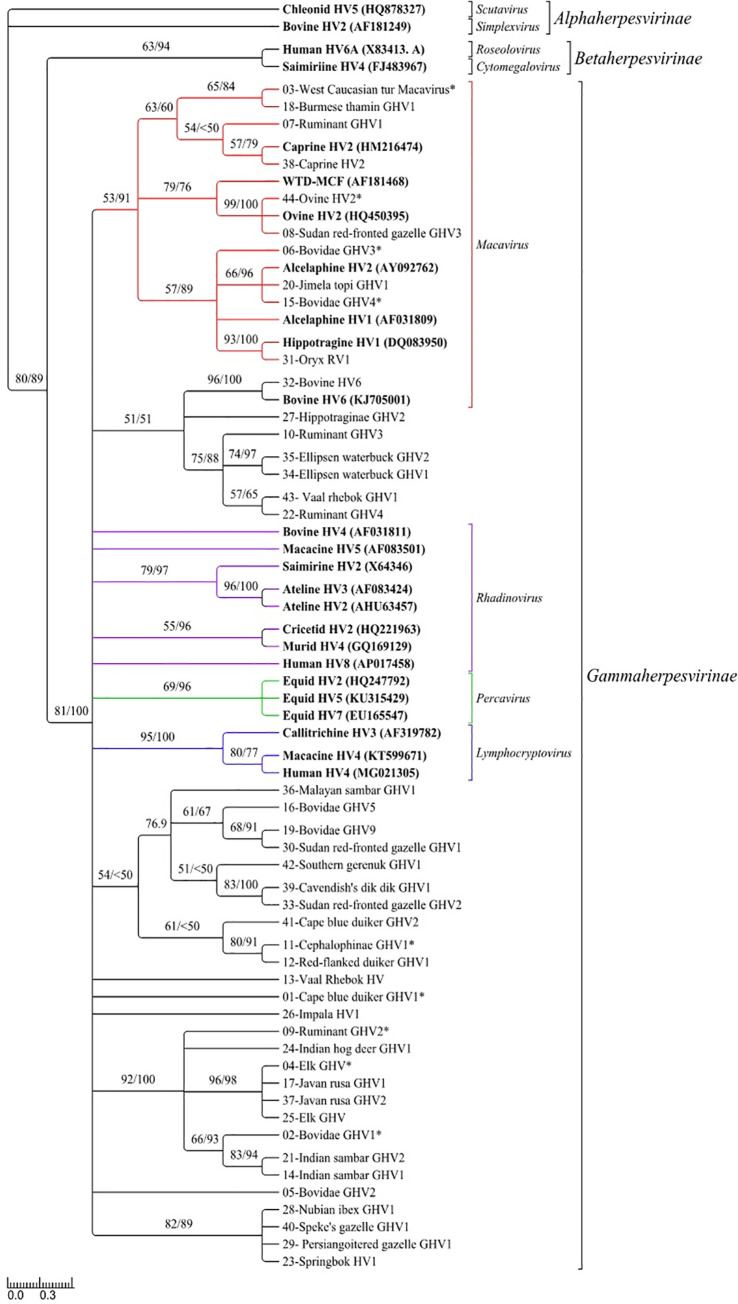
Fig 1. Phylogenetic relationships of translated amino acid sequences from DPOL genotypes detected in ruminant species from the San Diego Zoo or it's Safari Park using PCR.
The unrooted phylogenetic tree was constructed using translated amino acid sequences (71 aa) from DPOL genotypes in Table 3 and herpesviruses from GenBank. Accession numbers for each reference sequence are included in the figure. Maximum-likelihood bootstrap values are to the left of the slash ("/") and Bayesian Posterior Probabilities, expressed as a percentage, are to the right at each node. Nodes with Maximum-likelihood bootstrap values less than 50 were collapsed. The numerical DPOL genotype is followed by the provisional common name for new viral species or the previously described virus name from Table 3. DPOL genotypes obtained from clinical MCF cases are indicated with an asterisk (*), and references from GHV sub-families recognized by the International Committee on the Taxonomy of Viruses are indicated in bold. Known genera are indicated by color: red (Macavirus), purple (Rhadinovirus), blue (Lymphocryptovirus), and green (Percavirus). Known genus and sub-families are also indicated with brackets.