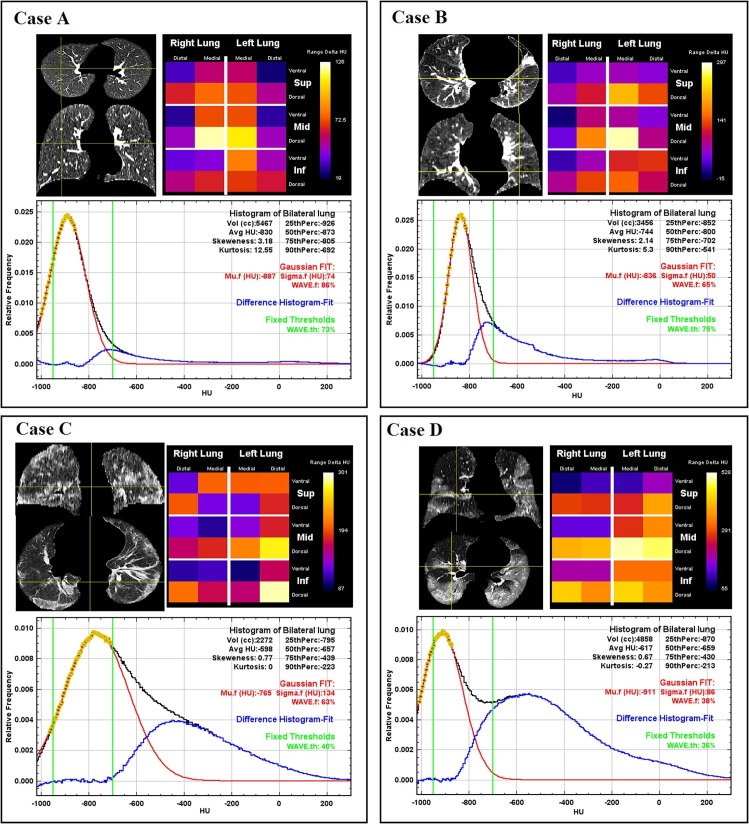
Fig. 5.
Examples of patients analyzed with the methods described in the materials and methods section. Segmented lungs are displayed in axial and coronal views. Local changes in density are reported in lungograms. In the plots, black curve represents the CT relative histogram of the entire lung. Yellow dots are the data points selected to calculate Gaussian fit (red curve). The difference between CT lung relative histogram and Gaussian fit is reported in blue while the HU range used for WAVE.th calculations is reported by two green vertical lines. The relative metrics are reported with the same colors as the curves in the graphs on which they are calculated. Lung histogram features (HU average, skewness, kurtosis, and percentiles) are reported in black, Gaussian fit parameters (Mu.f, Sigma.f) and WAVE.f are reported in red while WAVE.th is reported in green. Case A: example of healthy lung from dataset 1. The Gaussian fit is well overlapped to the CT relative histogram, with a slight deviation on the right side of the black curve, caused likely by the inclusion in the lung segmentation of major vessels. Case B: example of patient with cancer in the left lung, from dataset 2. The presence of the tumor mass and the consequent distortion of the surrounding structures increase the deviation between the Gaussian fit and the CT relative histogram. Case C: COVID-19 patient with an extended ground glass opacification of the lung that enlarges the Gaussian fit. In addition to the fact that Mu.f value is on the right side of the green window (-950/-700 HU), it causes an important difference between the two WAVE metrics. The lungogram shows that the higher values of the biomarker ΔHUMu-Avg are found in the dorsal regions. Case D: Widespread disease with only some portions of healthy lung, but sufficient to produce a suitable histogram for Gaussian fit. In this case, WAVE.f, and WAVE.th calculations returned similar results even if Mu.f value is not in the central position of the range used to calculate WAVE.th. The lungogram shows that the higher values of ΔHUMu-Avg are found in the dorsal regions. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)