Figure 7.
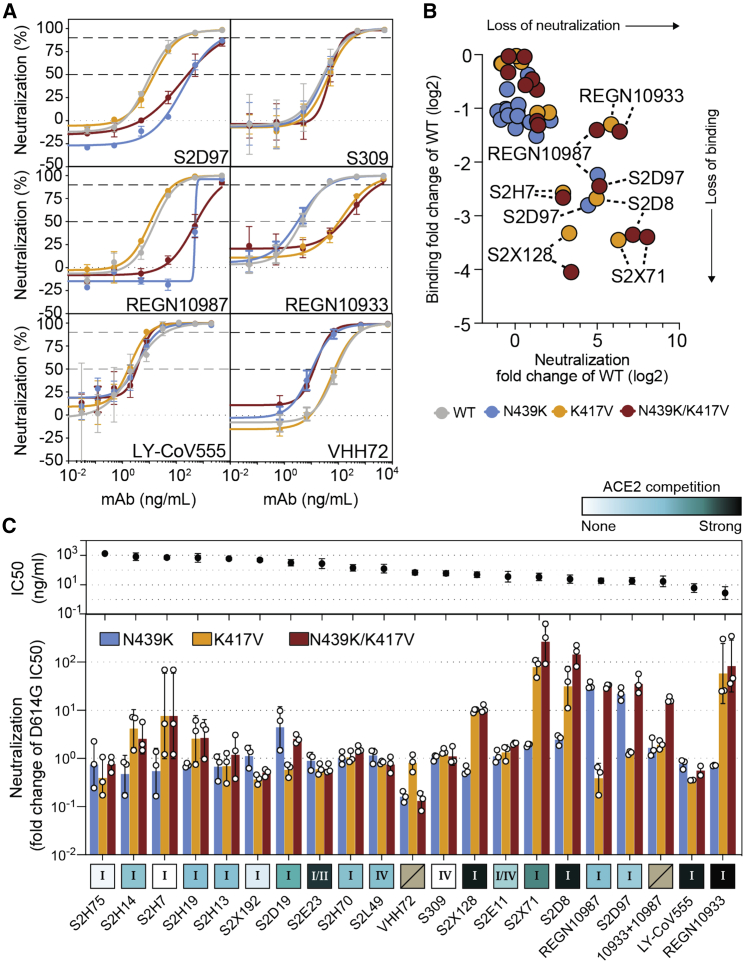
Neutralization of four RBM variants by a panel of antibodies and a nanobody
(A) Neutralization of four VSV-pseudovirus variants by six of the mAbs tested. Data shown are representative of n = 3 biological replicates, bars = SD of technical duplicate (Data S1).
(B) Correlation of ELISA-binding fold change and neutralization fold change for each variant relative to WT.
(C) Top: neutralization IC50 of the D614G virus determined as the geometric mean of three biological replicates. Bottom: neutralization results for all mAbs tested, expressed as a fold-change relative to D614G (all variants are in the background of D614G) (Data S1). The individual values of the three replicates are shown as open circles, their geometric mean as colored bars and the geometric SD as error bars. Each antibody is annotated according to its hACE2 competition (as shown in Figure 6F) as well as its epitope (site I, II, or IV) (Data S1). Gray boxes with a slash indicate not tested for hACE2 competition or epitope analysis.
See also Figure S7.