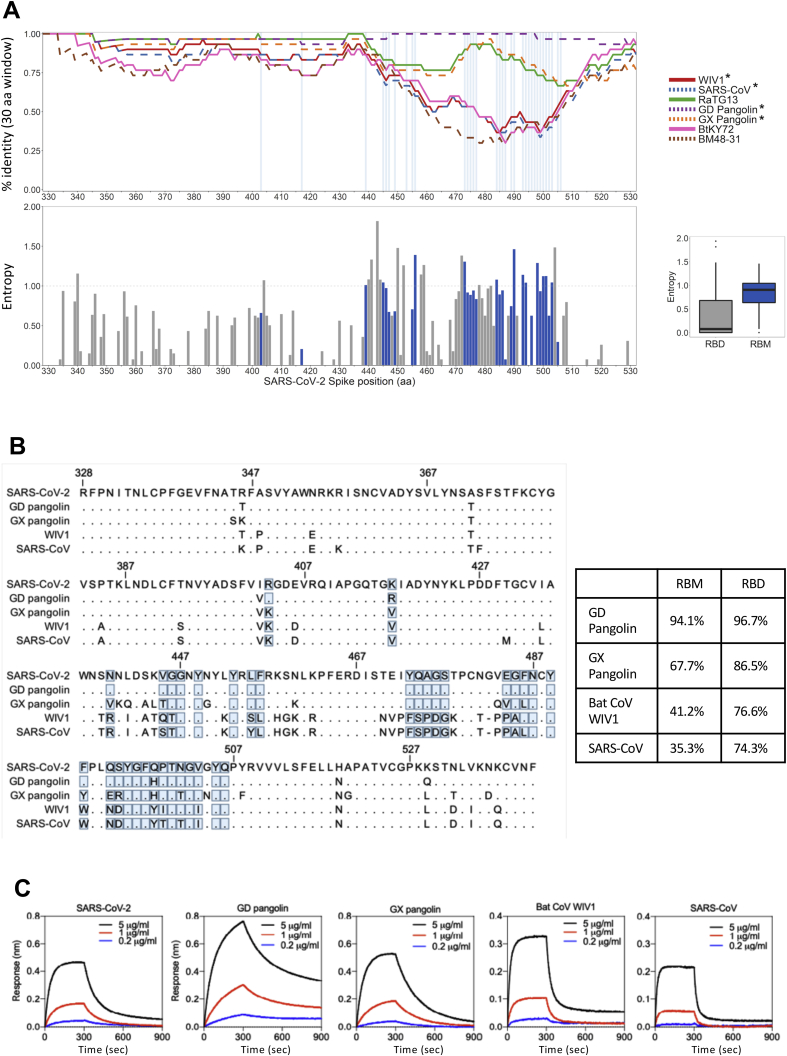
Figure S2.
RBDs from bat and pangolin Sarbecovirus isolates bind to hACE2 despite RBM divergence, related to Figures 1 and 2
(A) Top – Percent identity to SARS-CoV-2 using a sliding window size of 30 amino acids for seven related Sarbecoviruses (see figure key, ∗: viruses which bind to hACE2) across the RBD region of the Spike protein. Bottom – Site-specific entropy plot across the RBD protein alignment of SARS-CoV-2 and 68 related viruses (Table S1). Sites constituting the RBM are annotated in blue; the x axis refers to absolute positions in the SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein sequence. Right – boxplot of site-specific entropy values for the RBM sites (blue) and the full RBD (gray).
(B) Sequence alignment (left) and identity for RBM and RBD (right) to SARS-CoV-2 of the RBD sequences showing binding to hACE2. RBM residues indicated by blue boxes.
(C) Binding of hACE2 to human, pangolin, and bat Sarbecovirus RBDs by BLI. Bat CoV RaTG13, Bat CoVs ZC45, BtKY72 and BGR2008 have also been tested and did not bind hACE2.