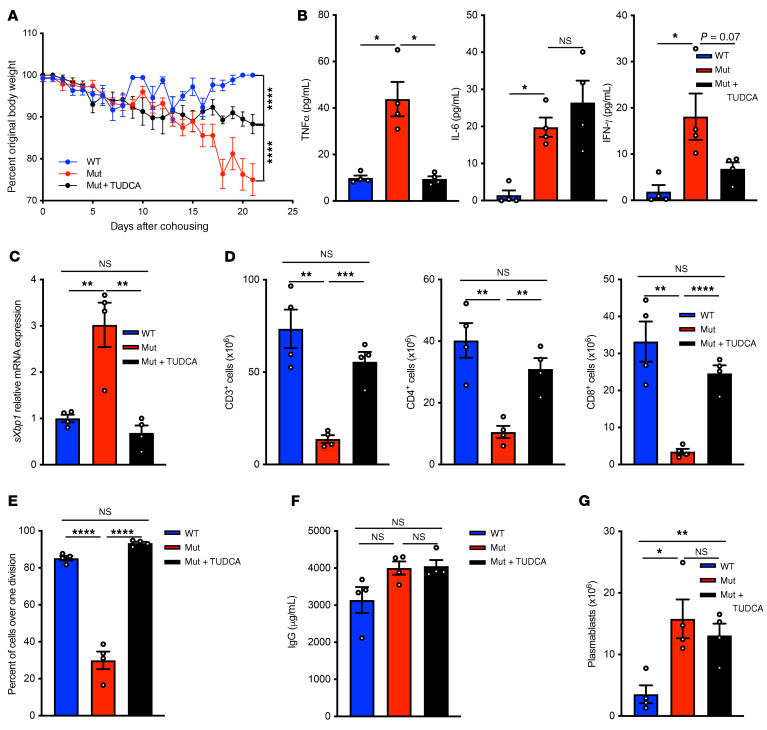
Figure 7. Treatment of Copg1K652E mutant mice with TUDCA partially reverses the phenotype induced by microbial exposure.
Mutant mice received TUDCA or vehicle daily for 21 days starting on day 0 of cohousing. In the same experiment, a group of WT mice were cohoused with pet store mice as control. (A) Weight expressed as percentage of body weight at day 0 of cohousing. (B) Serum TNF-α, IL-6, and IFN-γ levels on day 21. (C) Splenocyte expression of sXbp1 on day 21. Values are relative to gene expression of cohoused WT mice. (D) Numbers of viable CD3+, CD4+, and CD8+ T cells in the spleens on day 21. (E) Proliferation of purified splenic T cells in response to αCD3+αCD28 stimulation on day 21. (F and G) Serum IgG levels (F) and numbers of B220loCD138+ plasmablasts in the spleens (G) on day 21. Results for A and G were pooled from 2 independent experiments each with 4 mice/group. Columns and bars represent mean and SEM. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001; ****P ≤ 0.0001, 2-way ANOVA (A); Holm-Šídák test to control for multiple comparisons (B and G).