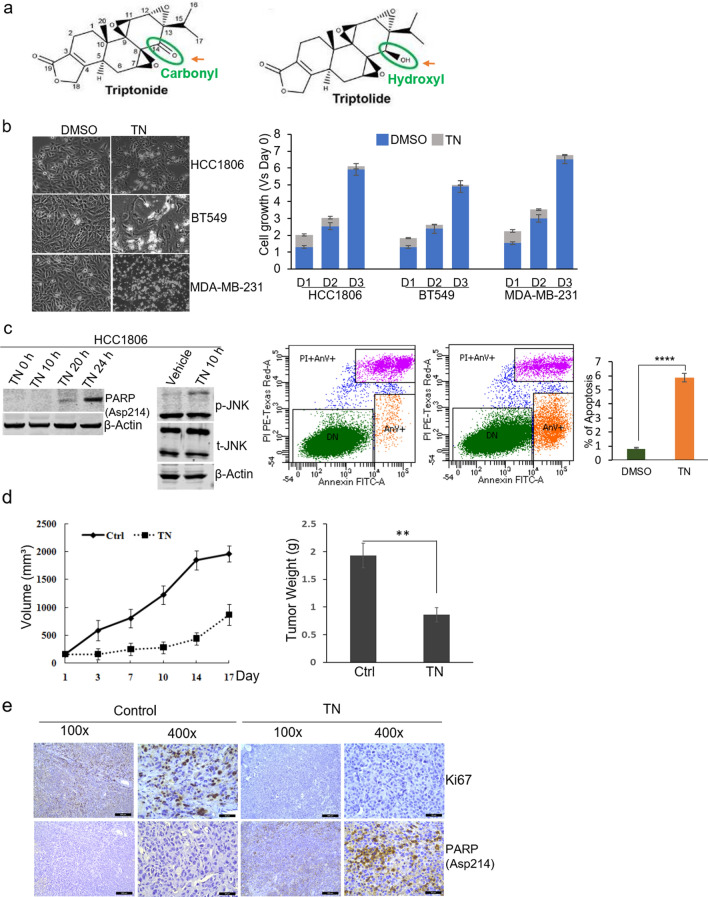
Figure 1.
Triptonide inhibits TNBC cell growth in vitro and in vivo. (a) Chemical structures of triptonide and triptolide. (b) Left, representative images showing the effects of 0.2 µM triptonide treatment for 24-h in HCC1806, BT549, and MDA-MB-231 cells. Magnification, × 200. Right, quantified effects of 0.2 µM triptonide on cell growth measured by CellTiter-Glo assays. HCC1806, BT549, and MDA-MB-231 cells were treated for 24 h (D1), 48 h (D2) and 72 h (D3). Each bar is presented as mean ± SD (n = 3). (c) Left, immunoblotting of p-JNK, total (t)-JNK, cleaved PARP in HCC1806 cells treated with 0.2 µM triptonide. Right, apoptosis analysis of HCC1806 cells treated with 0.2 µM triptonide for 20 h by the FITC Annexin V/PI apoptosis assay. (d) Comparisons of MDA-MB-231 xenograft mammary tumors in mice treated with vehicle or triptonide. Graphs show tumor volume changes with time and tumor weight at harvest. Each bar is presented as mean ± SD (n = 4). **, p < 0.01. (e) Expression of Ki67 and cleaved PARP in MDA-MB-231 xenograft tumor tissues examined by immunohistochemistry assays. Magnification, × 400.