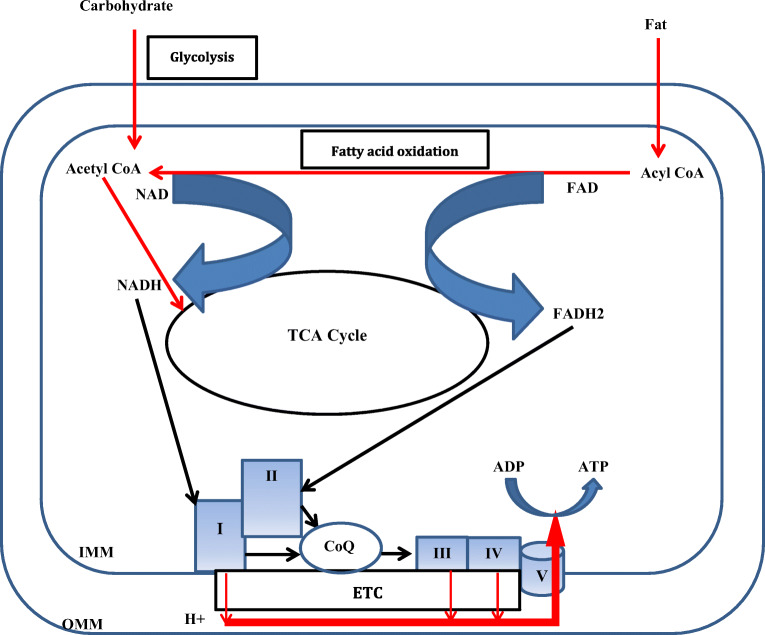
Fig. 1.
Diagrammatic representation of the role of mitochondria in energy metabolism inside cell. I: Complex I; II: Complex II; III: Complex III, IV: Complex IV; V: Complex V; CoQ: Coenzyme Q; ETC: Electron transport chain; FAD: Flavin adenine dinucleotide; IMM: Inner mitochondrial membrane; NAD: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide; OMM: Outer mitochondrial membrane; TCA: Tricarboxylic acid. Energy stored in food constituents are captured by NAD and FAD. The high energy electrons are then transferred to ETC where it gradually moves from high energy state to low energy state. The energy released in this process is harnessed to propel protons across the IMM creating a proton gradient across the IMM. Protons then diffuse along its concentration gradient at V. The energy released in this process is harnessed to generated ATP from ADP